Proteomic identification of small, copper-responsive proteins in germinating embryos of Oryza sativa
- PMID: 19201764
- PMCID: PMC2707895
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcp012
Proteomic identification of small, copper-responsive proteins in germinating embryos of Oryza sativa
Abstract
Background and aims: Although copper (Cu) is an essential micronutrient for plants and algae, excess Cu is toxic to most plants and can cause a wide range of deleterious effects. To investigate the response of rice (Oryza sativa) to Cu stress, a proteomic approach was used to analyse Cu stress-induced changes in the expression of low molecular-weight proteins in germinating rice seed embryos.
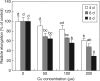
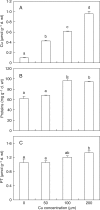
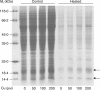
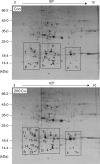
Methods: Rice seeds were germinated in the presence or absence of 200 microm Cu for 6 d, and embryos, including newly formed shoots and radicles, were isolated. After proteins were extracted from the germinating embryos and separated by two-dimensional PAGE, 16 proteins in the 6- to 25-kDa range were identified using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
Key results and conclusions: Thirteen of the proteins identified, including metallothionein-like protein, membrane-associated protein-like protein, putative wall-associated protein kinase, pathogenesis-related proteins and the putative small GTP-binding protein Rab2, were up-regulated by Cu stress. Three proteins, a putative small cytochrome P450 (CYP90D2), a putative thioredoxin and a putative GTPase, were down-regulated by Cu stress. As far as is known, this study provides the first proteomic evidence that metallothionein and CYP90D2 are Cu-responsive proteins in plants. These findings may lead to a better understanding of plant molecular responses to toxic metal exposure.
Figures

References
-
- Abbasi FM, Komatsu S. A proteomic approach to analyze salt-responsive proteins in rice leaf sheath. Proteomics. 2004;4:2072–2081. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal GK, Rakwal R, Yonekura M, Kubo A, Saji H. Proteome analysis of differentially displayed proteins as a tool for investigating ozone stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Proteomics. 2002;2:947–959. - PubMed
-
- Ahsan N, Lee DG, Lee SH, et al. Excess copper induced physiological and proteomic changes in germinating rice seeds. Chemosphere. 2007;67:1182–1193. - PubMed
-
- Bajguz A. Blockage of heavy metal accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris cells by 24-epibrassinolide. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. 2000;38:797–801.
-
- Berthet B, Mouneyrac C, Pérez T, Amiard-Triquet C. Metallothionein concentration in sponges (Spongia officinalis) as a biomarker of metal contamination. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology. 2005;141:306–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

