Identification of an rsh gene from a Novosphingobium sp. necessary for quorum-sensing signal accumulation
- PMID: 19201802
- PMCID: PMC2668395
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01692-08
Identification of an rsh gene from a Novosphingobium sp. necessary for quorum-sensing signal accumulation
Abstract
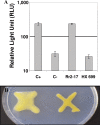
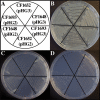
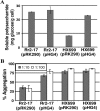
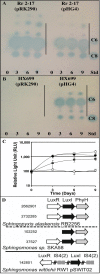
The stringent response is a mechanism by which bacteria adapt to environmental stresses and nutritional deficiencies through the synthesis and hydrolysis of (p)ppGpp by RelA/SpoT enzymes. Alphaproteobacteria and plants contain a single Rsh enzyme (named for RelA/SpoT homolog) that is bifunctional. Here we report the identification of a new species of bacteria belonging to the genus Novosphingobium and characterization of an rsh mutation in this plant tumor-associated isolate. Isolate Rr 2-17, from a grapevine crown gall tumor, is a member of the Novosphingobium genus that produces the N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) quorum-sensing (QS) signals. A Tn5 mutant, Hx 699, deficient in AHL production was found to have an insertion in an rsh gene. The Rsh protein showed significant percent sequence identity to Rsh proteins of alphaproteobacteria. The Novosphingobium sp. rsh gene (rsh(Nsp)) complemented the multiple amino acid requirements of the Escherichia coli relA spoT double mutant by restoring the growth on selection media. Besides QS signal production, the rsh mutation also affects soluble polysaccharide production and cell aggregation. Genetic complementation of the Hx 699 mutant with the rsh(Nsp) gene restored these phenotypes. This is the first discovery of a functional rsh gene in a member of the Novosphingobium genus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Novosphingobium pentaromativorans US6-1 Reveals the Rsh Regulon and Potential Molecular Mechanisms of N-acyl-l-homoserine Lactone Accumulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 5;19(9):2631. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092631. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30189641 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing signals of the grapevine crown gall bacterium, Novosphingobium sp. Rr2-17: use of inducible expression and polymeric resin to sequester acyl-homoserine lactones.PeerJ. 2024 Dec 20;12:e18657. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18657. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39735558 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequence of Novosphingobium sp. strain Rr 2-17, a nopaline crown gall-associated bacterium isolated from Vitis vinifera L. grapevine.J Bacteriol. 2012 Sep;194(18):5137-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.01159-12. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22933764 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing: how bacteria can coordinate activity and synchronize their response to external signals?Protein Sci. 2012 Oct;21(10):1403-17. doi: 10.1002/pro.2132. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Protein Sci. 2012. PMID: 22825856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms and Applications of N-Acyl Homoserine Lactone-Mediated Quorum Sensing in Bacteria.Molecules. 2022 Nov 4;27(21):7584. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217584. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Novosphingobium pentaromativorans US6-1 Reveals the Rsh Regulon and Potential Molecular Mechanisms of N-acyl-l-homoserine Lactone Accumulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 5;19(9):2631. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092631. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30189641 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequencing-assisted identification and the first functional validation of N-acyl-homoserine-lactone synthases from the Sphingomonadaceae family.PeerJ. 2016 Aug 30;4:e2332. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2332. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 27635318 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome sequencing and analysis reveal insights into the genetic structure, diversity and evolutionary relatedness of luxI and luxR homologs in bacteria belonging to the Sphingomonadaceae family.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Jan 8;4:188. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00188. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25621282 Free PMC article.
-
ppGpp conjures bacterial virulence.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2010 Jun;74(2):171-99. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00046-09. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20508246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of six bacteria belonging to the genus Novosphingobium: insights into marine adaptation, cell-cell signaling and bioremediation.BMC Genomics. 2013 Jun 28;14:431. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-431. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23809012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aravind, L., and E. V. Koonin. 1998. The HD domain defines a new superfamily of metal dependent phosphohydrolases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23469-472. - PubMed
-
- Braeken, K., M. Moris, R. Daniels, J. Vanderleyden, and J. Michiels. 2006. New horizons for (p)ppGpp in bacterial and plant physiology. Trends Microbiol. 1445-54. - PubMed
-
- Burr, T. J., C. Bazzi, S. Süle, and L. Otten. 1998. Crown gall of grape: biology of Agrobacterium vitis and the development of disease control strategies. Plant Dis. 821288-1297. - PubMed
-
- Calderon-Flores, A., G. Du Pont, A. Huerta-Saquero, H. Merchant-Larios, L. Servin-Gonzalez, and S. Duran. 2005. The stringent response is required for amino acid and nitrate utilization, Nod factor regulation, nodulation, and nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium etli. J. Bacteriol. 1875075-5083. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Case, R. J., M. Labbate, and S. Kejelleberg. 2008. AHL-driven quorum-sensing circuits: their frequency and function among the Proteobacteria. ISME J. 2345-349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

