Ozone modulates IL-6 secretion in human airway epithelial and smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 19201813
- PMCID: PMC3286236
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.90585.2008
Ozone modulates IL-6 secretion in human airway epithelial and smooth muscle cells
Abstract
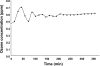
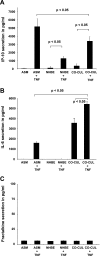
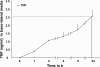
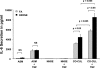
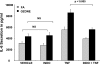
Although ozone enhances leukocyte function and recruitment in airways, the direct effect of ozone in modulating structural cell-derived inflammatory mediators remains unknown. Using a coculture model comprised of differentiated human airway epithelial cells (NHBE) and smooth muscle cells (ASM), we postulate that ozone regulates IL-6 secretion in basal and cytokine-primed structural cells. Air-liquid interface (ALI) cultures of NHBE cells underwent differentiation as determined by mucin secretion, transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER), and ultrastructure parameters. Whereas TNF enhanced basal secretion of IL-6 (57 +/- 3%), ozone exposure at 0.6 ppm for 6 h augmented IL-6 levels in basal (41 +/- 3%) and TNF- (50 +/- 5%) primed cocultures compared with that derived from NHBE or ASM monolayers alone. Levels of PGE(2), 6-keto-PGF(1alpha), PGF(2alpha), and thromboxane B(2) (TxB(2)) levels in basal and TNF-primed cocultures revealed that ozone selectively enhanced PGE(2) production in TNF- (6 +/- 3-fold) primed cocultures, with little effect (P > 0.05) on diluent-treated cultures. In accordance with ozone-induced increases in PGE(2) levels, cyclooxygenase inhibition with indomethacin partially abolished IL-6 secretion. Surprisingly, indomethacin had little effect on constitutive secretion of IL-6 in cocultures, whereas indomethacin completely restored ozone-mediated TEER reduction in TNF-primed cocultures. Collectively, our data for the first time suggest a dual role of ozone in modulating IL-6 secretion and TEER outcomes in a PGE(2)-dependent (in presence of TNF stimulus) and -independent manner (in absence of cytokine stimulus).
Figures
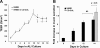

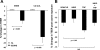
References
-
- Alpert SE, Walenga RW. Ozone exposure of human tracheal epithelial cells inactivates cyclooxygenase and increases 15-HETE production. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 269: L734–L743, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Amrani Y, Krymskaya V, Maki C, Panettieri RA Jr. Mechanisms underlying TNFα effects on agonist-mediated calcium homeostasis in human airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 273: L1020–L1028, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Amrani Y, Tliba O, Deshpande DA, Walseth TF, Kannan MS, Panettieri RA Jr. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness: insights into new signaling molecules. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4: 230–234, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JM, Van Itallie CM. Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 269: G467–G475, 1995. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

