The sequestosome 1/p62 attenuates cytokine gene expression in activated macrophages by inhibiting IFN regulatory factor 8 and TNF receptor-associated factor 6/NF-kappaB activity
- PMID: 19201866
- PMCID: PMC4151355
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802755
The sequestosome 1/p62 attenuates cytokine gene expression in activated macrophages by inhibiting IFN regulatory factor 8 and TNF receptor-associated factor 6/NF-kappaB activity
Abstract
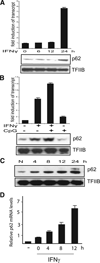
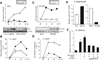
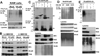
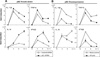
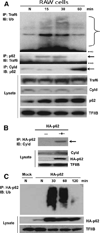
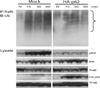
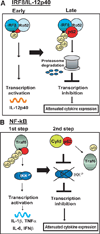
Sequestosome 1/p62 (p62) is a scaffold/adaptor protein with multiple functions implicated for neuronal and bone diseases. It carries a ubiquitin binding domain through which it mediates proteasome-dependent proteolysis. In addition, p62 is reported to regulate NF-kappaB activity in some cells. To date, however, the role of p62 in innate immunity has not been fully elucidated. In this study, we report that IFN-gamma plus TLR signaling stimulates late expression of p62 in murine macrophages. Overexpression of p62 inhibited expression of multiple cytokines, IL-12p40, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6, and IFN-beta, whereas p62 underexpression by small hairpin RNA markedly elevated their expression, indicating that p62 is a broad negative regulator of cytokine expression in stimulated macrophages. We show that p62 interacts with IFN regulatory factor 8 and Ro52, the transcription factor and ubiquitin E3 ligase that are important for IL-12p40 expression. This interaction, detectable at a late stage in stimulated macrophages, led to increased polyubiquitination and destabilization of IFN regulatory factor 8. We also show that upon macrophage stimulation, p62 binds to TNFR-associated factor 6, another E3 ligase important for NF-kappaB activation, but later this interaction was replaced by the recruitment of the deubiquitinating enzyme, cylindromatosis, an inhibitor of NF-kappaB activity. Recruitment of cylindromatosis coincided with reduced TNFR-associated factor 6 autoubiquitination and lower NF-kappaB activation. Our results indicate that p62 orchestrates orderly regulation of ubiquitin modification processes in macrophages to ensure attenuation of cytokine transcription postactivation. Together, p62 may provide a mechanism by which to control excessive inflammatory responses after macrophage activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TRAF6-mediated ubiquitination of NEMO requires p62/sequestosome-1.Mol Immunol. 2014 Mar;58(1):27-31. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.10.015. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Mol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24270048 Free PMC article.
-
The p62 scaffold regulates nerve growth factor-induced NF-kappaB activation by influencing TRAF6 polyubiquitination.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 21;280(42):35625-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C500237200. Epub 2005 Aug 3. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16079148
-
Inhibition of interleukin-12 p40 transcription and NF-kappaB activation by nitric oxide in murine macrophages and dendritic cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Mar 12;279(11):10776-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313416200. Epub 2003 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14679201
-
Inflammatory signaling in macrophages: transitions from acute to tolerant and alternative activation states.Eur J Immunol. 2011 Sep;41(9):2477-81. doi: 10.1002/eji.201141783. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21952800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p62: a versatile multitasker takes on cancer.Trends Biochem Sci. 2012 Jun;37(6):230-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2012.02.008. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012. PMID: 22424619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TRIM21 Ubiquitylates SQSTM1/p62 and Suppresses Protein Sequestration to Regulate Redox Homeostasis.Mol Cell. 2016 Mar 3;61(5):720-733. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.007. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26942676 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB Restricts Inflammasome Activation via Elimination of Damaged Mitochondria.Cell. 2016 Feb 25;164(5):896-910. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.057. Cell. 2016. PMID: 26919428 Free PMC article.
-
p62 Negatively Regulates TLR4 Signaling via Functional Regulation of the TRAF6-ECSIT Complex.Immune Netw. 2019 Jun 12;19(3):e16. doi: 10.4110/in.2019.19.e16. eCollection 2019 Jun. Immune Netw. 2019. PMID: 31281713 Free PMC article.
-
p62/SQSTM1 enhances NOD2-mediated signaling and cytokine production through stabilizing NOD2 oligomerization.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057138. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437331 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating IRFs in IFN Driven Disease.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 29;10:325. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00325. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30984161 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

