TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) activates proinflammatory signaling pathways and gene expression through the activation of TGF-beta-activated kinase 1
- PMID: 19201899
- PMCID: PMC2652039
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803357
TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) activates proinflammatory signaling pathways and gene expression through the activation of TGF-beta-activated kinase 1
Abstract
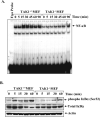
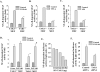
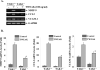
TWEAK, TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis, is a relatively recently identified proinflammatory cytokine that functions through binding to Fn14 receptor in target cells. Although TWEAK has been shown to modulate several biological responses, the TWEAK-induced signaling pathways remain poorly understood. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that TAK1 (TGF-beta-activated kinase 1) is involved in TWEAK-induced activation of NF-kappaB and MAPK and expression of proinflammatory protein. TWEAK increased the phosphorylation and kinase activity of TAK1 in cultured myoblast and fibroblast cells. The activation of NF-kappaB was significantly inhibited in TAK1-deficient (TAK1(-/-)) mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) compared with wild-type MEF. Deficiency of TAK1 also inhibited the TWEAK-induced activation of IkappaB kinase and the phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaBalpha protein. However, there was no difference in the levels of p100 protein in TWEAK-treated wild-type and TAK1(-/-) MEF. Furthermore, TWEAK-induced transcriptional activation of NF-kappaB was significantly reduced in TAK1(-/-) MEF and in C2C12 myoblasts transfected with a dominant-negative TAK1 or TAK1 short interfering RNA. TAK1 was also required for the activation of AP-1 in response to TWEAK. Activation of JNK1 and p38 MAPK, but not ERK1/2 or Akt kinase, was significantly inhibited in TAK1(-/-) MEF compared with wild-type MEF upon treatment with TWEAK. TWEAK-induced expression of proinflammatory genes such as MMP-9, CCL-2, and VCAM-1 was also reduced in TAK1(-/-) MEF compared with wild-type MEF. Furthermore, the activation of NF-kappaB and the expression of MMP-9 in response to TWEAK involved the upstream activation of Akt kinase. Collectively, our study demonstrates that TAK1 and Akt are the important components of TWEAK-induced proinflammatory signaling and gene expression.
Figures






References
-
- Aggarwal BB. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:745–756. - PubMed
-
- Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell. 2001;104:487–501. - PubMed
-
- Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H, Hsu YM, Scott H, Hession C, Garcia I, Browning JL. TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32401–32410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

