TNFalpha-dependent hepatic steatosis and liver degeneration caused by mutation of zebrafish S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase
- PMID: 19201949
- PMCID: PMC2685951
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.027565
TNFalpha-dependent hepatic steatosis and liver degeneration caused by mutation of zebrafish S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase
Abstract
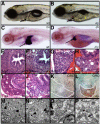
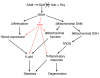
Hepatic steatosis and liver degeneration are prominent features of the zebrafish ducttrip (dtp) mutant phenotype. Positional cloning identified a causative mutation in the gene encoding S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (Ahcy). Reduced Ahcy activity in dtp mutants led to elevated levels of S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) and, to a lesser degree, of its metabolic precursor S-adenosylmethionine (SAM). Elevated SAH in dtp larvae was associated with mitochondrial defects and increased expression of tnfa and pparg, an ortholog of the mammalian lipogenic gene. Antisense knockdown of tnfa rescued hepatic steatosis and liver degeneration in dtp larvae, whereas the overexpression of tnfa and the hepatic phenotype were unchanged in dtp larvae reared under germ-free conditions. These data identify an essential role for tnfa in the mutant phenotype and suggest a direct link between SAH-induced methylation defects and TNF expression in human liver disorders associated with elevated TNFalpha. Although heterozygous dtp larvae had no discernible phenotype, hepatic steatosis was present in heterozygous adult dtp fish and in wild-type adult fish treated with an Ahcy inhibitor. These data argue that AHCY polymorphisms and AHCY inhibitors, which have shown promise in treating autoimmunity and other disorders, may be a risk factor for steatosis, particularly in patients with diabetes, obesity and liver disorders such as hepatitis C infection. Supporting this idea, hepatic injury and steatosis have been noted in patients with recently discovered AHCY mutations.
Figures


 P<0.05; NS, not
significant (P=0.3). (D) Calculated SAM:SAH ratio for the four
conditions in C. Differences in the SAM:SAH ratio between B and D arise from
experimental variation. (E) Anti-methylcytosine (αMeC) slot blot
of genomic DNA derived from wild-type or dtp larvae, with Methylene
Blue counterstain (MeBl). (F) Western blot showing reduced levels of
methylated lysine residues (αMeK) in protein from dtp larvae;
actin provided a loading control (αactin).
P<0.05; NS, not
significant (P=0.3). (D) Calculated SAM:SAH ratio for the four
conditions in C. Differences in the SAM:SAH ratio between B and D arise from
experimental variation. (E) Anti-methylcytosine (αMeC) slot blot
of genomic DNA derived from wild-type or dtp larvae, with Methylene
Blue counterstain (MeBl). (F) Western blot showing reduced levels of
methylated lysine residues (αMeK) in protein from dtp larvae;
actin provided a loading control (αactin).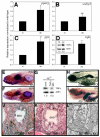


Similar articles
-
S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase over-expression does not alter S-adenosylmethionine or S-adenosylhomocysteine levels in CBS deficient mice.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2018 Jan 12;15:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2018.01.002. eCollection 2018 Jun. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2018. PMID: 30023284 Free PMC article.
-
Adult-onset liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma in S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase deficiency.Mol Genet Metab. 2015 Dec;116(4):269-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2015.10.009. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Mol Genet Metab. 2015. PMID: 26527160 Free PMC article.
-
Homeostatic generation of reactive oxygen species protects the zebrafish liver from steatosis.Hepatology. 2013 Oct;58(4):1326-38. doi: 10.1002/hep.26551. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23744565 Free PMC article.
-
Drinks like a fish: using zebrafish to understand alcoholic liver disease.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 May;35(5):826-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01407.x. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21284674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional and Pathological Roles of AHCY.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 31;9:654344. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.654344. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is produced by dying retinal neurons and is required for Muller glia proliferation during zebrafish retinal regeneration.J Neurosci. 2013 Apr 10;33(15):6524-39. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3838-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23575850 Free PMC article.
-
Translating discovery in zebrafish pancreatic development to human pancreatic cancer: biomarkers, targets, pathogenesis, and therapeutics.Zebrafish. 2013 Jun;10(2):132-46. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2012.0817. Epub 2013 May 17. Zebrafish. 2013. PMID: 23682805 Free PMC article.
-
High fat plus high cholesterol diet lead to hepatic steatosis in zebrafish larvae: a novel model for screening anti-hepatic steatosis drugs.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015 Nov 14;12:42. doi: 10.1186/s12986-015-0036-z. eCollection 2015. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26583037 Free PMC article.
-
S-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase (SAHH) accelerates flagellar regeneration in Dunaliella salina.Curr Microbiol. 2013 Aug;67(2):249-54. doi: 10.1007/s00284-013-0357-y. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Curr Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23532254
-
Zebrafish Discoveries in Cancer Epigenetics.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;916:169-97. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-30654-4_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27165354 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adinolfi, L. E., Ingrosso, D., Cesaro, G., Cimmino, A., D'Anto, M., Capasso, R., Zappia, V. and Ruggiero, G. (2005). Hyperhomocysteinemia and the MTHFR C677T polymorphism promote steatosis and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C patients. Hepatology 41, 995-1003. - PubMed
-
- Agger, K., Cloos, P. A., Christensen, J., Pasini, D., Rose, S., Rappsilber, J., Issaeva, I., Canaani, E., Salcini, A. E. and Helin, K. (2007). UTX and JMJD3 are histone H3K27 demethylases involved in HOX gene regulation and development. Nature 449, 731-734. - PubMed
-
- Agrimi, G., Di Noia, M. A., Marobbio, C. M., Fiermonte, G., Lasorsa, F. M. and Palmieri, F. (2004). Identification of the human mitochondrial S-adenosylmethionine transporter: bacterial expression, reconstitution, functional characterization and tissue distribution. Biochem. J. 379, 183-190. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

