Antimicrobial activity of the iron-sulfur nitroso compound Roussin's black salt [Fe4S3(NO)7] on the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus
- PMID: 19201977
- PMCID: PMC2663211
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02562-08
Antimicrobial activity of the iron-sulfur nitroso compound Roussin's black salt [Fe4S3(NO)7] on the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus
Abstract
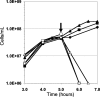
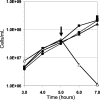
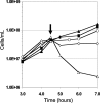
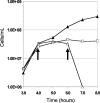
The iron-sulfur nitroso compound [Fe(4)S(3)(NO)(7)](-) is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent that has been used for more than 100 years to combat pathogenic anaerobes. Known as Roussin's black salt (RBS), it contains seven moles of nitric oxide, the release of which was always assumed to mediate its cytotoxicity. Using the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus, it is demonstrated through growth studies, membrane analyses, and scanning electron microscopy that nitric oxide does not play a role in RBS toxicity; rather, the mechanism involves membrane disruption leading to cell lysis. Moreover, insoluble elemental sulfur (S(0)), which is reduced by P. furiosus to hydrogen sulfide, prevents cell lysis by RBS. It is proposed that S(0) also directly interacts with the membranes of P. furiosus during its transfer into the cell, ultimately for reduction by a cytosolic NADPH sulfur reductase. RBS is proposed to be a new class of inorganic antimicrobial agent that also has potential use as an inert cell-lysing agent.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NO-dependent phototoxicity of Roussin's black salt against cancer cells.Nitric Oxide. 2004 Feb;10(1):42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2004.01.009. Nitric Oxide. 2004. PMID: 15050534
-
Insights into the metabolism of elemental sulfur by the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus: characterization of a coenzyme A- dependent NAD(P)H sulfur oxidoreductase.J Bacteriol. 2007 Jun;189(12):4431-41. doi: 10.1128/JB.00031-07. Epub 2007 Apr 20. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17449625 Free PMC article.
-
The elemental sulfur-responsive protein (SipA) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus is regulated by sulfide in an iron-dependent manner.J Bacteriol. 2010 Nov;192(21):5841-3. doi: 10.1128/JB.00660-10. Epub 2010 Aug 27. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20802041 Free PMC article.
-
The hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus utilizes environmental iron sulfide cluster complexes as an iron source.Extremophiles. 2021 May;25(3):249-256. doi: 10.1007/s00792-021-01224-1. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Extremophiles. 2021. PMID: 33779854
-
Sulfide dehydrogenase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus: a new multifunctional enzyme involved in the reduction of elemental sulfur.J Bacteriol. 1994 Nov;176(21):6509-17. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.21.6509-6517.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 7961401 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of protein-bound dinitrosyl iron complexes by nuclear resonance vibrational spectroscopy.J Am Chem Soc. 2010 May 26;132(20):6914-6. doi: 10.1021/ja101002f. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20429508 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Multinuclear Metal Nitrosyl Complexes.Coord Chem Rev. 2016 Jan 1;306(Pt 2):678-700. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2015.03.026. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Coord Chem Rev. 2016. PMID: 26744544 Free PMC article.
-
Caldicellulosiruptor obsidiansis sp. nov., an anaerobic, extremely thermophilic, cellulolytic bacterium isolated from Obsidian Pool, Yellowstone National Park.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Feb;76(4):1014-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01903-09. Epub 2009 Dec 18. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20023107 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial seafood packaging: a review.J Food Sci Technol. 2016 Jun;53(6):2505-18. doi: 10.1007/s13197-016-2216-x. Epub 2016 Jun 27. J Food Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 27478206 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ashworth, J., A. Didcock, L. L. Hargreaves, B. Jarvis, C. L. Walter, and L. F. Larkworthy. 1974. Chemical and microbiological comparisons of inhibitors derived thermally from nitrite with an iron thionitrosyl (Roussin black salt). J. Gen. Microbiol. 84:403-408. - PubMed
-
- Bourassa, J., B. Lee, S. Bernard, J. Schoonover, and P. C. Ford. 1999. Flash photolysis studies of Roussin's black salt anion: Fe4S3(NO)7−. Inorg. Chem. 38:2947-2952. - PubMed
-
- Butler, A. R., F. W. Flitney, and D. L. Williams. 1995. NO, nitrosonium ions, nitroxide ions, nitrosothiols and iron-nitrosyls in biology: a chemist's perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 16:18-22. - PubMed
-
- Cammack, R., C. L. Joannou, X. Y. Cui, C. Torres Martinez, S. R. Maraj, and M. N. Hughes. 1999. Nitrite and nitrosyl compounds in food preservation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1411:475-488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

