Modulation of DNA methylation by a sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide
- PMID: 19201992
- PMCID: PMC2672871
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.108.147934
Modulation of DNA methylation by a sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide
Abstract
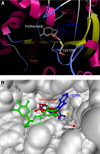
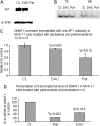
Hypermethylation of 5'-cytosine-guanosine islands of tumor suppressor genes resulting in their silencing has been proposed to be a hallmark of various tumors. Modulation of DNA methylation with DNA methylation inhibitors has been shown to result in cancer cell differentiation or apoptosis and represents a novel strategy for chemotherapy. Currently, effective DNA methylation inhibitors are mainly limited to decitabine and 5-azacytidine, which still show unfavorable toxicity profiles in the clinical setting. Thus, discovery and development of novel hypomethylating agents, with a more favorable toxicity profile, is essential to broaden the spectrum of epigenetic therapy. Parthenolide, the principal bioactive sesquiterpene lactone of feverfew, has been shown to alkylate Cys(38) of p65 to inhibit nuclear factor-kappaB activation and exhibit anti-tumor activity in human malignancies. In this article, we report that parthenolide 1) inhibits DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) with an IC(50) of 3.5 microM, possibly through alkylation of the proximal thiolate of Cys(1226) of the catalytic domain by its gamma-methylene lactone, and 2) down-regulates DNMT1 expression possibly associated with its SubG(1) cell-cycle arrest or the interruption of transcriptional factor Sp1 binding to the promoter of DNMT1. These dual functions of parthenolide result in the observed in vitro and in vivo global DNA hypomethylation. Furthermore, parthenolide has been shown to reactivate tumor suppressor HIN-1 gene in vitro possibly associated with its promoter hypomethylation. Hence, our study established parthenolide as an effective DNA methylation inhibitor, representing a novel prototype for DNMT1 inhibitor discovery and development from natural structural-diversified sesquiterpene lactones.
Figures


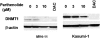



References
-
- Cheng JC, Matsen CB, Gonzales FA, Ye W, Greer S, Marquez VE, Jones PA, and Selker EU (2003) Inhibition of DNA methylation and reactivation of silenced genes by zebularine. J Natl Cancer Inst 95 399-409. - PubMed
-
- Cheng D, Xiao JJ, Cheng H, Liu Z, Covey JM, and Chan, KK (2005) Analytical method development and pharmacokinetics studies with parthenolide (NSC 157035) and a water-soluble analog (NSC 734325), in The Annual Meeting of the American Association of Cancer Research, Abstract number 4184, American Association of Cancer Research, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Chuang JC, Yoo CB, Kwan JM, Li TW, Liang G, Yang AS, and Jones PA (2005) Comparison of biological effects of non-nucleoside DNA methylation inhibitors versus 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine. Mol Cancer Ther 4 1515-1520. - PubMed
-
- Fang MZ, Wang Y, Ai N, Hou Z, Sun Y, Lu H, Welsh W, and Yang CS (2003) Tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits DNA methyltransferase and reactivates methylation-silenced genes in cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 63 7563-7570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

