Power of deep, all-exon resequencing for discovery of human trait genes
- PMID: 19202052
- PMCID: PMC2656172
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0812824106
Power of deep, all-exon resequencing for discovery of human trait genes
Abstract
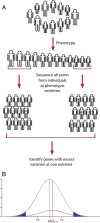
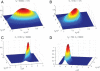
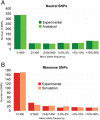
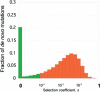
The ability to sequence cost-effectively all of the coding regions of a given individual genome is rapidly approaching, with the potential for whole-genome resequencing not far behind. Initiatives are currently underway to phenotype hundreds of thousands of individuals for major human traits. Here, we determine the power for de novo discovery of genes related to human traits by resequencing all human exons in a clinical population. We analyze the potential of the gene discovery strategy that combines multiple rare variants from the same gene and treats genes, rather than individual alleles, as the units for the association test. By using computer simulations based on deep resequencing data for the European population, we show that genes meaningfully affecting a human trait can be identified in an unbiased fashion, although large sample sizes would be required to achieve substantial power.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Couzin J, Kaiser J. Genome-wide association. Closing the net on common disease genes. Science. 2007;316:820–822. - PubMed
-
- Frayling TM. Genome-wide association studies provide new insights into type 2 diabetes aetiology. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:657–662. - PubMed
-
- Cohen JC, et al. Multiple rare alleles contribute to low plasma levels of HDL cholesterol. Science. 2004;305:869–872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

