Ndy1/KDM2B immortalizes mouse embryonic fibroblasts by repressing the Ink4a/Arf locus
- PMID: 19202064
- PMCID: PMC2650317
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0813139106
Ndy1/KDM2B immortalizes mouse embryonic fibroblasts by repressing the Ink4a/Arf locus
Abstract
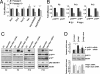
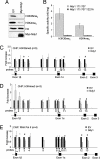
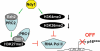
The histone H3 demethylase Not dead yet-1 (Ndy1/KDM2B) is a physiological inhibitor of senescence. Here, we show that Ndy1 is down-regulated during senescence in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and that it represses the Ink4a/Arf locus. Ndy1 counteracts the senescence-associated down-regulation of Ezh2, a component of polycomb-repressive complex (PRC) 2, via a JmjC domain-dependent process leading to the global and Ink4a/Arf locus-specific up-regulation of histone H3K27 trimethylation. The latter promotes the Ink4a/Arf locus-specific binding of Bmi1, a component of PRC1. Ndy1, which interacts with Ezh2, also binds the Ink4a/Arf locus and demethylates the locus-associated histone H3K36me2 and histone H3K4me3. The combination of histone modifications driven by Ndy1 interferes with the binding of RNA Polymerase II, resulting in the transcriptional silencing of the Ink4a/Arf locus and contributing to the Ndy1 immortalization phenotype. Other studies show that, in addition to inhibiting replicative senescence, Ndy1 inhibits Ras oncogene-induced senescence via a similar molecular mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
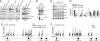
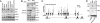
Similar articles
-
Polycomb mediated epigenetic silencing and replication timing at the INK4a/ARF locus during senescence.PLoS One. 2009 May 20;4(5):e5622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005622. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19462008 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine-specific demethylase 2B (KDM2B)-let-7-enhancer of zester homolog 2 (EZH2) pathway regulates cell cycle progression and senescence in primary cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 23;286(38):33061-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.257667. Epub 2011 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21757686 Free PMC article.
-
A novel zinc finger protein Zfp277 mediates transcriptional repression of the Ink4a/arf locus through polycomb repressive complex 1.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 24;5(8):e12373. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012373. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20808772 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA, polycomb, and the ghosts haunting INK4b-ARF-INK4a expression.Cancer Res. 2011 Aug 15;71(16):5365-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4379. Epub 2011 Aug 9. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21828241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Jun dimerization protein 2 controls senescence and differentiation via regulating histone modification.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:569034. doi: 10.1155/2011/569034. Epub 2010 Dec 12. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21197464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kdm2b promotes induced pluripotent stem cell generation by facilitating gene activation early in reprogramming.Nat Cell Biol. 2012 Apr 22;14(5):457-66. doi: 10.1038/ncb2483. Nat Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22522173 Free PMC article.
-
DNA binding by polycomb-group proteins: searching for the link to CpG islands.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 May 20;50(9):4813-4839. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac290. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35489059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of senescence upon loss of the Ash2l core subunit of H3K4 methyltransferase complexes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Aug 12;50(14):7889-7905. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac591. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35819198 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of KDM2B and EZH2 in Regulating the Stemness in Colorectal Cancer Through the PI3K/AKT Pathway.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 9;11:637298. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.637298. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33791221 Free PMC article.
-
The H3K4me3 histone demethylase Fbxl10 is a regulator of chemokine expression, cellular morphology, and the metabolome of fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 7;287(37):30984-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.341040. Epub 2012 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22825849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collado M, Blasco MA, Serrano M. Cellular senescence in cancer and aging. Cell. 2007;130:223–233. - PubMed
-
- Gil J, Peters G. Regulation of the INK4b-ARF-INK4a tumour suppressor locus: All for one or one for all. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:667–677. - PubMed
-
- Sharpless NE, et al. Loss of p16Ink4a with retention of p19Arf predisposes mice to tumorigenesis. Nature. 2001;413:86–91. - PubMed
-
- Serrano M, et al. Role of the INK4a locus in tumor suppression and cell mortality. Cell. 1996;85:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Kamijo T, et al. Tumor suppression at the mouse INK4a locus mediated by the alternative reading frame product p19ARF. Cell. 1997;91:649–659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

