Ndy1/KDM2B immortalizes mouse embryonic fibroblasts by repressing the Ink4a/Arf locus
- PMID: 19202064
- PMCID: PMC2650317
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0813139106
Ndy1/KDM2B immortalizes mouse embryonic fibroblasts by repressing the Ink4a/Arf locus
Abstract
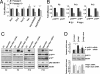
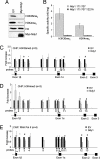
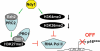
The histone H3 demethylase Not dead yet-1 (Ndy1/KDM2B) is a physiological inhibitor of senescence. Here, we show that Ndy1 is down-regulated during senescence in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and that it represses the Ink4a/Arf locus. Ndy1 counteracts the senescence-associated down-regulation of Ezh2, a component of polycomb-repressive complex (PRC) 2, via a JmjC domain-dependent process leading to the global and Ink4a/Arf locus-specific up-regulation of histone H3K27 trimethylation. The latter promotes the Ink4a/Arf locus-specific binding of Bmi1, a component of PRC1. Ndy1, which interacts with Ezh2, also binds the Ink4a/Arf locus and demethylates the locus-associated histone H3K36me2 and histone H3K4me3. The combination of histone modifications driven by Ndy1 interferes with the binding of RNA Polymerase II, resulting in the transcriptional silencing of the Ink4a/Arf locus and contributing to the Ndy1 immortalization phenotype. Other studies show that, in addition to inhibiting replicative senescence, Ndy1 inhibits Ras oncogene-induced senescence via a similar molecular mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
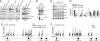
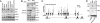
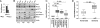
References
-
- Collado M, Blasco MA, Serrano M. Cellular senescence in cancer and aging. Cell. 2007;130:223–233. - PubMed
-
- Gil J, Peters G. Regulation of the INK4b-ARF-INK4a tumour suppressor locus: All for one or one for all. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:667–677. - PubMed
-
- Sharpless NE, et al. Loss of p16Ink4a with retention of p19Arf predisposes mice to tumorigenesis. Nature. 2001;413:86–91. - PubMed
-
- Serrano M, et al. Role of the INK4a locus in tumor suppression and cell mortality. Cell. 1996;85:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Kamijo T, et al. Tumor suppression at the mouse INK4a locus mediated by the alternative reading frame product p19ARF. Cell. 1997;91:649–659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

