Potassium softens vascular endothelium and increases nitric oxide release
- PMID: 19202069
- PMCID: PMC2637279
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0813069106
Potassium softens vascular endothelium and increases nitric oxide release
Abstract
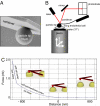
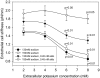
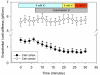
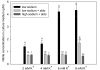
In the presence of aldosterone, plasma sodium in the high physiological range stiffens endothelial cells and reduces the release of nitric oxide. We now demonstrate effects of extracellular potassium on stiffness of individual cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells by using the tip of an atomic force microscope as a mechanical nanosensor. An acute increase of potassium in the physiological range swells and softens the endothelial cell and increases the release of nitric oxide. A high physiological sodium concentration, in the presence of aldosterone, prevents these changes. We propose that the potassium effects are caused by submembranous cortical fluidization because cortical actin depolymerization induced by cytochalasin D mimics the effect of high potassium. In contrast, a low dose of trypsin, known to activate sodium influx through epithelial sodium channels, stiffens the submembranous cell cortex. Obviously, the cortical actin cytoskeleton switches from gelation to solation depending on the ambient sodium and potassium concentrations, whereas the center of the cell is not involved. Such a mechanism would control endothelial deformability and nitric oxide release, and thus influence systemic blood pressure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Roson MI, et al. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats. Kidney Int. 2006;70:1439–1446. - PubMed
-
- Ni Z, Vaziri ND. Effect of salt loading on nitric oxide synthase expression in normotensive rats. Am J Hypertens. 2001;14:155–163. - PubMed
-
- Mercier N, et al. Sodium, arterial stiffness, and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens. 2007;20:319–325. - PubMed
-
- Frohlich ED, Varagic J. Sodium directly impairs target organ function in hypertension. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2005;20:424–429. - PubMed
-
- Adrogue HJ, Madias NE. Sodium and potassium in the pathogenesis of hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1966–1978. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

