Methylphenidate-induced dendritic spine formation and DeltaFosB expression in nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 19202072
- PMCID: PMC2650365
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0813179106
Methylphenidate-induced dendritic spine formation and DeltaFosB expression in nucleus accumbens
Abstract
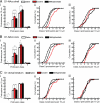
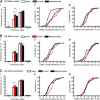
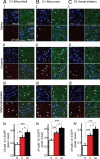
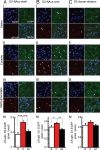
Methylphenidate is the psychostimulant medication most commonly prescribed to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Recent trends in the high usage of methylphenidate for both therapeutic and nontherapeutic purposes prompted us to investigate the long-term effects of exposure to the drug on neuronal adaptation. We compared the effects of chronic methylphenidate or cocaine (15 mg/kg, 14 days for both) exposure in mice on dendritic spine morphology and DeltaFosB expression in medium-sized spiny neurons (MSN) from ventral and dorsal striatum. Chronic methylphenidate increased the density of dendritic spines in MSN-D1 (MSN-expressing dopamine D1 receptors) from the core and shell of nucleus accumbens (NAcc) as well as MSN-D2 (MSN-expressing dopamine D2 receptors) from the shell of NAcc. In contrast, cocaine increased the density of spines in both populations of MSN from all regions of striatum. In general, the effect of methylphenidate on the increase of shorter spines (class 2) was less than that of cocaine. Interestingly, the methylphenidate-induced increase in the density of relatively longer spines (class 3) in the shell of NAcc was bigger than that induced by cocaine. Furthermore, methylphenidate exposure increased expression of DeltaFosB only in MSN-D1 from all areas of striatum, and surprisingly, the increase was greater than that induced by cocaine. Thus, our results show differential effects of methylphenidate and cocaine on neuronal adaptation in specific types of MSN in reward-related brain regions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Biederman J, Faraone SV. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet. 2005;366:237–248. - PubMed
-
- Robison LM, Sclar DA, Skaer TL, Galin RS. National trends in the prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and the prescribing of methylphenidate among school-age children: 1990–1995. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1999;38:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Volkow ND, et al. Dopamine transporter occupancies in the human brain induced by therapeutic doses of oral methylphenidate. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155:1325–1331. - PubMed
-
- Volkow ND, et al. Is methylphenidate like cocaine? Studies on their pharmacokinetics and distribution in the human brain. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995;52:456–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

