Interferometric fluorescent super-resolution microscopy resolves 3D cellular ultrastructure
- PMID: 19202073
- PMCID: PMC2637278
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0813131106
Interferometric fluorescent super-resolution microscopy resolves 3D cellular ultrastructure
Abstract
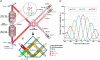
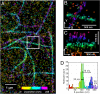
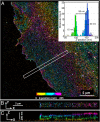
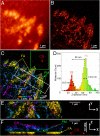
Understanding molecular-scale architecture of cells requires determination of 3D locations of specific proteins with accuracy matching their nanometer-length scale. Existing electron and light microscopy techniques are limited either in molecular specificity or resolution. Here, we introduce interferometric photoactivated localization microscopy (iPALM), the combination of photoactivated localization microscopy with single-photon, simultaneous multiphase interferometry that provides sub-20-nm 3D protein localization with optimal molecular specificity. We demonstrate measurement of the 25-nm microtubule diameter, resolve the dorsal and ventral plasma membranes, and visualize the arrangement of integrin receptors within endoplasmic reticulum and adhesion complexes, 3D protein organization previously resolved only by electron microscopy. iPALM thus closes the gap between electron tomography and light microscopy, enabling both molecular specification and resolution of cellular nanoarchitecture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

