Anti-CTLA-4 therapy results in higher CD4+ICOShi T cell frequency and IFN-gamma levels in both nonmalignant and malignant prostate tissues
- PMID: 19202079
- PMCID: PMC2650334
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0813175106
Anti-CTLA-4 therapy results in higher CD4+ICOShi T cell frequency and IFN-gamma levels in both nonmalignant and malignant prostate tissues
Abstract
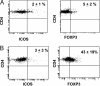
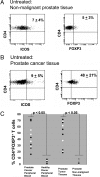
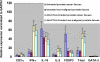
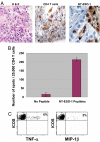
Cytotoxic lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) blockade is an active immunotherapeutic strategy that is currently in clinical trials in cancer. There are several ongoing trials of anti-CTLA-4 in the metastatic setting of prostate cancer patients with reported clinical responses consisting of decreases in the prostate specific antigen (PSA) tumor marker for some patients. Immunologic markers that correlate with these clinical responses are necessary to guide further development of anti-CTLA-4 therapy in the treatment of cancer patients. We recently reported that CD4(+) inducible co-stimulator (ICOS)(hi) T cells that produce interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) are increased in the peripheral blood and tumor tissues of bladder cancer patients treated with anti-CTLA-4 antibody. Here we present data from the same clinical trial in bladder cancer patients demonstrating a higher frequency of CD4(+)ICOS(hi) T cells and IFN-gamma mRNA levels in nonmalignant prostate tissues and incidental prostate tumor tissues removed at the time of radical cystoprostatectomy. Our data suggest immunologic markers that can be used to monitor prostate cancer patients who receive anti-CTLA-4 therapy and indicate that the immunologic impact of anti-CTLA-4 antibody can occur in both tumor and nonmalignant tissues. These data should be taken into consideration for evaluation of efficacy as well as immune-related adverse events associated with anti-CTLA-4 therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: P.S. has served as a consultant on advisory boards for Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Figures

References
-
- Walunas TL, et al. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994;1:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Leach DR, Krummel MF, Allison JP. Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science. 1996;271:1734–1736. - PubMed
-
- van Elas A, Hurwitz AA, Allison JP. Combination immunotherapy of B16 melanoma using anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)-producing vaccines induces rejection of subcutaneous and metastatic tumors accompanied by autoimmune depigmentation. J Exp Med. 1999;190:355–366. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

