Production of a unique pneumococcal capsule serotype belonging to serogroup 6
- PMID: 19202106
- PMCID: PMC3706093
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.024521-0
Production of a unique pneumococcal capsule serotype belonging to serogroup 6
Abstract
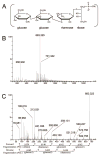
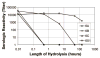
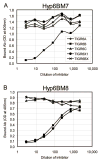
Serogroup 6 of Streptococcus pneumoniae contains three serotypes, named 6A, 6B and 6C, with highly homologous capsule gene loci. The 6A and 6B capsule gene loci consistently differ from each other by only one nucleotide in the wciP gene. The 6A capsule gene locus has a galactosyltransferase, which has been replaced with a glucosyltransferase in the 6C capsule gene locus. We considered that a new serotype named '6X1' would be possible if the galactosyltransferase of the 6B capsule gene locus is replaced with the glucosyltransferase of 6C. We demonstrate that this gene transfer yields a viable pneumococcal strain and that the capsular polysaccharide (PS) from this strain has the predicted chemical structure and serological similarity to the capsular PS of the 6B serotype. The new strain (i.e. serotype 6X1) is typed as 6B by the quellung reaction, but it can be distinguished from 6B strains with mAbs to 6B PS. Reexamination of 264 pneumococcal isolates that had been previously typed as 6B with classical typing methods revealed no isolates expressing serotype 6X1. Nevertheless, this study shows that this capsular PS is biochemically possible and could exist/emerge in nature.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of capsular genes of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6A, 6B, 6C, and 6D isolates.J Clin Microbiol. 2011 May;49(5):1758-64. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02628-10. Epub 2011 Mar 16. J Clin Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21411593 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic, biochemical, and serological characterization of a new pneumococcal serotype, 6H, and generation of a pneumococcal strain producing three different capsular repeat units.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015 Mar;22(3):313-8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00647-14. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25589550 Free PMC article.
-
Capsular polysaccharide gene diversity of pneumococcal serotypes 6A, 6B, 6C, and 6D.Int J Med Microbiol. 2014 Nov;304(8):1109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25220816
-
Current methods for capsular typing of Streptococcus pneumoniae.J Microbiol Methods. 2015 Jun;113:41-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 25. J Microbiol Methods. 2015. PMID: 25819558 Review.
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae Capsular Polysaccharide.Microbiol Spectr. 2019 Mar;7(2):10.1128/microbiolspec.gpp3-0019-2018. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0019-2018. Microbiol Spectr. 2019. PMID: 30977464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How many factor antisera can be found for serogroup 6 Streptococcus pneumoniae?J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Aug;48(8):3046; author reply 3046-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00643-10. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20668300 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prevalence and genetic structures of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6D, South Korea.Emerg Infect Dis. 2010 Nov;16(11):1751-3. doi: 10.3201/eid1611.100941. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 21029535 Free PMC article.
-
First report of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6D in South America.J Clin Microbiol. 2011 May;49(5):2080-1. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00153-11. Epub 2011 Mar 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21430101 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cross-reactivity of current serogroup 6 factor sera from Statens Serum Institut with the recently described pneumococcal serotype 6d.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Aug;48(8):3044-5. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00839-10. Epub 2010 Jun 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20573866 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Update on the evolving landscape of pneumococcal capsule types: new discoveries and way forward.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2025 Mar 13;38(1):e0017524. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00175-24. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39878373 Review.
References
-
- Cole R. Treatment of pneumonia by means of specific serums. JAMA. 1913;61:663–666.
-
- Fedson DS. Pneumococcal Vaccine. In: Plotkin SA, Mortimer EA, editors. Vaccines. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co; 1988. pp. 271–299.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

