Honokiol, a multifunctional antiangiogenic and antitumor agent
- PMID: 19203212
- PMCID: PMC2842137
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2009.2440
Honokiol, a multifunctional antiangiogenic and antitumor agent
Abstract
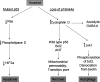
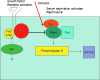
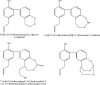
Honokiol is a small-molecule polyphenol isolated from the genus Magnolia. It is accompanied by other related polyphenols, including magnolol, with which it shares certain biologic properties. Recently, honokiol has been found to have antiangiogenic, antiinflammatory, and antitumor properties in preclinical models, without appreciable toxicity. These findings have increased interest in bringing honokiol to the clinic as a novel chemotherapeutic agent. In addition, mechanistic studies have tried to find the mechanism(s) of action of honokiol, for two major reasons. First, knowledge of the mechanisms of action may assist development of novel synthetic analogues. Second, mechanistic actions of honokiol may lead to rational combinations with conventional chemotherapy or radiation for enhanced response to systemic cancers. In this review, we describe the findings that honokiol has two major mechanisms of action. First, it blocks signaling in tumors with defective p53 function and activated ras by directly blocking the activation of phospholipase D by activated ras. Second, honokiol induces cyclophilin D, thus potentiating the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, and causing death in cells with wild-type p53. Knowledge of the dual activities of honokiol can assist with the development of honokiol derivatives and the design of clinical trials that will maximize the potential benefit of honokiol in the patient setting.
Figures


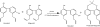
Similar articles
-
Honokiol and magnolol as multifunctional antioxidative molecules for dermatologic disorders.Molecules. 2010 Sep 16;15(9):6452-65. doi: 10.3390/molecules15096452. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20877235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Honokiol induces a necrotic cell death through the mitochondrial permeability transition pore.Cancer Res. 2007 May 15;67(10):4894-903. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3818. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17510419
-
Structural modification of honokiol, a biphenyl occurring in Magnolia officinalis: the evaluation of honokiol analogues as inhibitors of angiogenesis and for their cytotoxicity and structure-activity relationship.J Med Chem. 2011 Oct 13;54(19):6469-81. doi: 10.1021/jm200830u. Epub 2011 Sep 8. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21853991
-
Magnolol and honokiol from Magnolia officinalis enhanced antiviral immune responses against grass carp reovirus in Ctenopharyngodon idella kidney cells.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017 Apr;63:245-254. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.02.020. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28232195
-
Natural Lignans Honokiol and Magnolol as Potential Anticarcinogenic and Anticancer Agents. A Comprehensive Mechanistic Review.Nutr Cancer. 2022;74(3):761-778. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2021.1931364. Epub 2021 May 28. Nutr Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34047218 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular protection of magnolol: cell-type specificity and dose-related effects.J Biomed Sci. 2012 Jul 31;19(1):70. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-70. J Biomed Sci. 2012. PMID: 22849814 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of magnolol targeting both RXRα and PPARγ.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e28253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028253. Epub 2011 Nov 29. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22140563 Free PMC article.
-
Honokiol ameliorates endothelial dysfunction through suppression of PTX3 expression, a key mediator of IKK/IκB/NF-κB, in atherosclerotic cell model.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Jul 3;47(7):e171. doi: 10.1038/emm.2015.37. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26138903 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain/SHP-1 interaction by honokiol dampening peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer in nu/nu mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43711. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043711. Epub 2012 Aug 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22937084 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of honokiol against oxidative stress-induced apoptotic signaling in mouse podocytes treated with H2O2.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Aug;16(2):1278-1284. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6313. Epub 2018 Jun 14. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30116378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn KS. Sethi G. Shishodia S. Sung B. Arbiser JL. Aggarwal BB. Honokiol potentiates apoptosis, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and inhibits invasion through modulation of nuclear factor-kappaB activation pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 2006;4:621–633. - PubMed
-
- Ai J. Wang X. Nielsen M. Honokiol and magnolol selectively interact with GABAA receptor subtypes in vitro. Pharmacology. 2001;63:34–41. - PubMed
-
- Aoshima H. Hamamoto K. Potentiation of GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes by perfume and phytoncid. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1999;63:743–748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

