The effect of single and combined activating killer immunoglobulin-like receptor genotypes on cytomegalovirus infection and immunity after hematopoietic cell transplantation
- PMID: 19203722
- PMCID: PMC2770248
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2008.11.030
The effect of single and combined activating killer immunoglobulin-like receptor genotypes on cytomegalovirus infection and immunity after hematopoietic cell transplantation
Abstract
It has been shown that activating killer Ig-like receptor (aKIR) genes are important for control of cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). To date, using the broad classification of KIR haplotypes A and B, the precise role of individual KIR genes in the control of infection cannot be discerned. To address this, a consecutive case series of 211 non-T cell-depleted HCT patients all at risk for CMV were monitored biweekly for CMV DNA in plasma by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (Q-PCR) and at intervals for CMV-specific T cell immunity. Comparing patients with CMV reactivation (n = 152) to those with no reactivation (n = 59), the presence of specific aKIR haplotypes in the donor, but not in the recipient, were associated with protection from CMV reactivation and control of peak plasma CMV DNA (P < .001). A donor aKIR profile, predictive for low risk of CMV reactivation, contained either aKIR2DS2 and aKIR2DS4 or had >/=5 aKIR genes. Neither donor nor recipient inhibitory KIR (iKIR) played a role in a protective effect. CD4(+)- and CD8(+)-specific CMV immunity did not explain reduced CMV infection. The initial control of CMV infection after HCT is managed by aKIR functions, and donor aKIR haplotypes deserve further evaluation in donor selection for optimized HCT outcome.
Figures
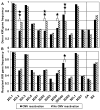
 n=59, having no CMV reactivation). The KIR gene frequency is separately portrayed for donors (Panel A) and recipients (Panel B). aKIR2DS4d represents the deletion variant of aKIR2DS4. iKIR2DL4, iKIR3DL2 and iKIR3DL3 were detected in all members of this cohort, and thus omitted from this figure. AA indicates individuals homozygous for KIR haplotype A, and BX indicates individuals either heterozygous (BA) or homozygous (BB) for KIR haplotype B. * p= 0.06, ** p≤ 0.05 using the Chi-square test.
n=59, having no CMV reactivation). The KIR gene frequency is separately portrayed for donors (Panel A) and recipients (Panel B). aKIR2DS4d represents the deletion variant of aKIR2DS4. iKIR2DL4, iKIR3DL2 and iKIR3DL3 were detected in all members of this cohort, and thus omitted from this figure. AA indicates individuals homozygous for KIR haplotype A, and BX indicates individuals either heterozygous (BA) or homozygous (BB) for KIR haplotype B. * p= 0.06, ** p≤ 0.05 using the Chi-square test.


References
-
- Lanier LL. NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:225–274. - PubMed
-
- Gerosa F, Gobbi A, Zorzi P, et al. The reciprocal interaction of NK cells with plasmacytoid or myeloid dendritic cells profoundly affects innate resistance functions. J Immunol. 2005;174:727–734. - PubMed
-
- Moretta A, Marcenaro E, Parolini S, Ferlazzo G, Moretta L. NK cells at the interface between innate and adaptive immunity. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15:226–233. - PubMed
-
- Vilches C, Parham P. KIR: diverse, rapidly evolving receptors of innate and adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:217–251. - PubMed
-
- Carrington M, Martin MP. The impact of variation at the KIR gene cluster on human disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;298:225–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

