Epidermal growth factor-activated aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator/HIF-1{beta} signal pathway up-regulates cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression associated with squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 19203995
- PMCID: PMC2665114
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806210200
Epidermal growth factor-activated aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator/HIF-1{beta} signal pathway up-regulates cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression associated with squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
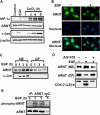
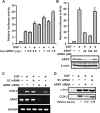
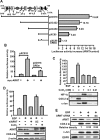
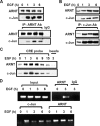
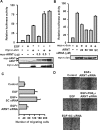
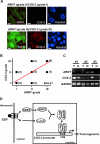
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) accumulates when tumors grow under hypoxic conditions. The genesis of tumors, however, usually involves normoxic conditions. In this study, we were interested in examining the potential role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT)/HIF-1beta in tumor growth under normoxic conditions, specifically when cells are treated with epidermal growth factor (EGF), which is known to affect the gene expression of tumor growth-related protein COX-2 (cyclooxygenase-2). The results showed that EGF receptor inhibitor, AG1478, abolished EGF-induced nuclear accumulation of ARNT as well as the expression of COX-2. ARNT small interfering RNA inhibited the promoter activity, mRNA level, and protein expression of COX-2 in cells treated with EGF. In contrast, CoCl(2)-induced HIF-1alpha exhibited no effect on COX-2 expression. EGF also stimulated the formation of the ARNT.c-Jun complex as well as the complex binding to the COX-2 promoter. ARNT small interfering RNAs blocked EGF-activated cell migration. Moreover, COX-2 and ARNT were cohorts present distinctively in clinical specimens of human cervical squamous cell carcinoma and were almost nondetectable in adjacent normal or noncancerous cervical tissues. Our results revealed that ARNT plays an important role in EGF-regulated COX-2 gene expression and may thus be related to either a cause or a consequence of tumorigenesis in cervical cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator in EGF-induced c-Jun/Sp1-mediated gene expression.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Oct;67(20):3523-33. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0392-9. Epub 2010 May 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20508969 Free PMC article.
-
The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Nuclear Translocator (ARNT/HIF-1β) is influenced by hypoxia and hypoxia-mimetics.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(4):849-58. doi: 10.1159/000354487. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 24081025
-
Curcumin inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1 by degrading aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator: a mechanism of tumor growth inhibition.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;70(5):1664-71. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.025817. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16880289
-
Hypoxia-inducible aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) (HIF-1β): is it a rare exception?Mol Med. 2014 May 27;20(1):215-20. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2014.00032. Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24849811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of HIF-1alpha at the transcriptional level.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(33):3844-52. doi: 10.2174/138161209789649420. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19671046 Review.
Cited by
-
ARNT deficiency represses pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 to trigger ROS production and melanoma metastasis.Oncogenesis. 2021 Jan 14;10(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-00299-3. Oncogenesis. 2021. PMID: 33446631 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator in EGF-induced c-Jun/Sp1-mediated gene expression.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Oct;67(20):3523-33. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0392-9. Epub 2010 May 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20508969 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptin-derived peptide reverses cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer through the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway.Cancer Med. 2018 Apr;7(4):1369-1383. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1380. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 29522284 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor protects squamous cell carcinoma against cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity through increased interleukin-1β expression.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055795. Epub 2013 Feb 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383347 Free PMC article.
-
The novel Aryl hydrocarbon receptor inhibitor biseugenol inhibits gastric tumor growth and peritoneal dissemination.Oncotarget. 2014 Sep 15;5(17):7788-804. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2307. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25226618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kewley, R. J., Whitelaw, M. L., and Chapman-Smith, A. (2004) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36 189–204 - PubMed
-
- Giaccia, A., Siim, B. G., and Johnson, R. S. (2003) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2 803–811 - PubMed
-
- Kozak, K. R., Abbott, B., and Hankinson, O. (1997) Dev. Biol. 191 297–305 - PubMed
-
- Maltepe, E., Schmidt, J. V., Baunoch, D., Bradfield, C. A., and Simon, M. C. (1997) Nature 386 403–407 - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet, P., Dor, Y., Herbert, J-M., Fukumura, D., Brusselmans, K., Dewerchin, M., Neeman, M., Bono, F., Abramovitch, R., Maxwell, P., Koch, C. J., Ratcliffe, P., Moons, L., Jain, R. K., Collen, D., and Keshet, E. (1998) Nature 394 485–490 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

