Polymorphisms in erythrocyte binding antigens 140 and 181 affect function and binding but not receptor specificity in Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 19204093
- PMCID: PMC2663147
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01331-08
Polymorphisms in erythrocyte binding antigens 140 and 181 affect function and binding but not receptor specificity in Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
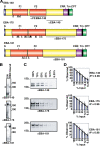
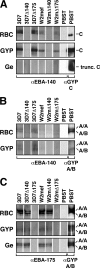
Invasion of human erythrocytes by the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum utilizes multiple ligand-receptor interactions involving erythrocyte receptors and parasite erythrocyte binding proteins of the Duffy binding-like family. Erythrocyte binding antigen 175 (EBA-175) binds to glycophorin A, the most abundant protein on the human erythrocyte surface and EBA-140 (also known as BAEBL) binds to glycophorin C, while the receptor for EBA-181 (also known as JESEBL) remains unknown. EBA binding is mediated via region II, a highly structured extracellular domain that shows a degree of sequence variability between different laboratory strains/isolates. Here, we determined the influence of region II polymorphisms on host cell receptor binding and overall function during invasion of EBA-140, EBA-175, and EBA-181. Polymorphisms in the binding domains of EBA-140 and EBA-181 have been suggested previously to alter their respective receptor specificities. In our hands, these polymorphisms affected the levels of EBA-140 and EBA-181 binding to receptors but, critically, not the receptor specificities of these proteins. The degree of EBA-140 binding to glycophorin C correlates with the level of function for this ligand-receptor interaction in merozoite invasion. In contrast, EBA-175, which is highly polymorphic in region II, shows no variability in its ability to bind to its receptor, glycophorin A. Combined, these data highlight the importance of sequence variability in EBAs as driven by immune selection but not by receptor specificity.
Figures


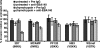
Similar articles
-
Baculovirus-expressed Plasmodium reichenowi EBA-140 merozoite ligand is host specific.Parasitol Int. 2016 Dec;65(6 Pt A):708-714. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2016.07.009. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Parasitol Int. 2016. PMID: 27443851
-
A novel Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte binding protein-2 (EBP2/BAEBL) involved in erythrocyte receptor binding.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002 Feb;119(2):159-68. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(01)00428-5. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002. PMID: 11814568
-
Plasmodium reichenowi EBA-140 merozoite ligand binds to glycophorin D on chimpanzee red blood cells, shedding new light on origins of Plasmodium falciparum.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Nov 7;10(1):554. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2507-8. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 29115972 Free PMC article.
-
Erythrocyte glycophorins as receptors for Plasmodium merozoites.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Jun 24;12(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3575-8. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31234897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Human erythrocyte glycophorin C as the receptor for EBA-140 Plasmodium falciparum merozoite ligand].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2013 Dec 23;67:1331-9. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1081865. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2013. PMID: 24379273 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Genetic diversity and neutral selection in Plasmodium vivax erythrocyte binding protein correlates with patient antigenicity.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Jul 9;14(7):e0008202. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008202. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32645098 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Invasion Mechanisms and Host Immune Response to Plasmodium vivax Malaria: Trends and Future Directions.Microorganisms. 2020 Dec 23;9(1):15. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010015. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33374596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasmodium falciparum BAEBL binds to heparan sulfate proteoglycans on the human erythrocyte surface.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 15;285(3):1716-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.021576. Epub 2009 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19940142 Free PMC article.
-
The Cellular and Molecular Interaction Between Erythrocytes and Plasmodium falciparum Merozoites.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Mar 31;12:816574. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.816574. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35433504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reticulocyte and erythrocyte binding-like proteins function cooperatively in invasion of human erythrocytes by malaria parasites.Infect Immun. 2011 Mar;79(3):1107-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01021-10. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21149582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, J. H., P. L. Blair, O. Kaneko, and D. S. Peterson. 2001. An expanding ebl family of Plasmodium falciparum. Trends Parasitol. 17297-299. - PubMed
-
- Barnwell, J. W., and M. R. Galinski. 1998. Invasion of vertebrate cells: erythrocytes, p. 93-120. In I. W. Sherman (ed.), Malaria: parasite biology, pathogenesis and protection. ASM Press, Washington DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

