Effects of the selective estrogen receptor modulator raloxifene on coronary outcomes in the Raloxifene Use for The Heart trial: results of subgroup analyses by age and other factors
- PMID: 19204301
- PMCID: PMC3673562
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.817577
Effects of the selective estrogen receptor modulator raloxifene on coronary outcomes in the Raloxifene Use for The Heart trial: results of subgroup analyses by age and other factors
Abstract
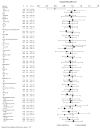
Background: The Raloxifene Use for The Heart (RUTH) trial showed that raloxifene, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, had no overall effect on the incidence of coronary events in women with established coronary heart disease or coronary heart disease risk factors. We provide detailed results of the effect of raloxifene on coronary outcomes over time and for 24 subgroups (17 predefined, 7 post hoc).
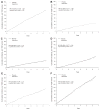
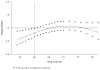
Methods and results: Postmenopausal women (n=10 101; mean age, 67 years) were randomized to raloxifene 60 mg/d or placebo for a median of 5.6 years. Coronary outcomes were assessed by treatment group in women with coronary heart disease risk factors and those with established coronary heart disease. Raloxifene had no effect on the incidence of coronary events in any subgroup except in the case of a post hoc age subgroup analysis using age categories defined in the Women's Health Initiative randomized trials. The effect of raloxifene on the incidence of coronary events differed significantly by age (interaction P=0.0118). The incidence of coronary events in women <60 years of age was significantly lower in those assigned raloxifene (50 events) compared with placebo (84 events; hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.41 to 0.83; P=0.003; absolute risk reduction, 36 per 1000 women treated for 1 year). No difference was found between treatment groups in the incidence of coronary events in women > or =60 and <70 or > or =70 years of age.
Conclusions: In postmenopausal women at increased risk of coronary events, the overall lack of benefit of raloxifene was similar across the prespecified subgroups.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00190593.
Figures

Comment in
-
On looking at subgroups.Circulation. 2009 Feb 24;119(7):912-5. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.836601. Circulation. 2009. PMID: 19237669 No abstract available.
-
Letter by Choi et al regarding article, "Effects of the selective estrogen receptor modulator raloxifene on coronary outcomes in the raloxifene use for the heart trial: results of subgroup analyses by age and other factors".Circulation. 2009 Oct 27;120(17):e147; author reply e148. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.857573. Circulation. 2009. PMID: 19858421 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ettinger B, Black DM, Mitlak BH, Knickerbocker RK, Nickelsen T, Genant HK, Christiansen C, Delmas PD, Zanchetta JR, Stakkestad J, Gluer CC, Krueger K, Cohen FJ, Eckert S, Ensrud KE, Avioli LV, Lips P, Cummings SR. Reduction of vertebral fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis treated with raloxifene: results from a 3-year randomized clinical trial: Multiple Outcomes of Raloxifene Evaluation (MORE) Investigators. JAMA. 1999;282:637–645. - PubMed
-
- Cummings SR, Eckert S, Krueger KA, Grady D, Powles TJ, Cauley JA, Norton L, Nickelsen T, Bjarnason NH, Morrow M, Lippman ME, Black D, Glusman JE, Costa A, Jordan VC. The effect of raloxifene on risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women: results from the MORE randomized trial: Multiple Outcomes of Raloxifene Evaluation. JAMA. 1999;281:2189–2197. - PubMed
-
- Martino S, Cauley JA, Barrett-Connor E, Powles TJ, Mershon J, Disch D, Secrest RJ, Cummings SR. Continuing outcomes relevant to Evista: breast cancer incidence in postmenopausal osteoporotic women in a randomized trial of raloxifene. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:1751–1761. - PubMed
-
- Barrett-Connor E, Mosca L, Collins P, Geiger MJ, Grady D, Kornitzer M, McNabb MA, Wenger NK. Effects of raloxifene on cardiovascular events and breast cancer in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:125–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

