SK2 potassium channel overexpression in basolateral amygdala reduces anxiety, stress-induced corticosterone secretion and dendritic arborization
- PMID: 19204724
- PMCID: PMC2763614
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2009.9
SK2 potassium channel overexpression in basolateral amygdala reduces anxiety, stress-induced corticosterone secretion and dendritic arborization
Abstract
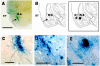
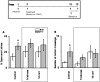
The basolateral amygdala is critical for generation of anxiety. In addition, exposure to both stress and glucocorticoids induces anxiety. Demonstrated ability of the amygdala to change in response to stress and glucocorticoids could thus be important therapeutic target for anxiety management. Several studies have reported a relationship between anxiety and dendritic arborization of the amygdaloid neurons. In this study we employed a gene therapeutic approach to reduce anxiety and dendritic arborization of the amygdala neurons. Specifically, we overexpressed SK2 potassium channel in the basolateral amygdala using a herpes simplex viral system. Our choice of therapeutic cargo was guided by the indications that activation of the amygdala might underlie anxiety and that SK2 could reduce neuronal activation by exerting inhibitory influence on action potentials. We report that SK2 overexpression reduced anxiety and stress-induced corticosterone secretion at a systemic level. SK2 overexpression also reduced dendritic arborization of the amygdala neurons. Hence, SK2 is a potential gene therapy candidate molecule that can be used against stress-related neuropsychiatric disorders such as anxiety.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor overexpression in basolateral amygdala reduces corticosterone secretion and anxiety.Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Oct 1;66(7):686-90. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.04.016. Epub 2009 Jun 5. Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19500777
-
Toxoplasma gondii infection induces dendritic retraction in basolateral amygdala accompanied by reduced corticosterone secretion.Dis Model Mech. 2013 Mar;6(2):516-20. doi: 10.1242/dmm.009928. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Dis Model Mech. 2013. PMID: 23104989 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery after chronic stress fails to reverse amygdaloid neuronal hypertrophy and enhanced anxiety-like behavior.Neuroscience. 2004;128(4):667-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.07.013. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15464275
-
Expression of chimeric estrogen-glucocorticoid-receptor in the amygdala reduces anxiety.Brain Res. 2010 Jun 25;1342:33-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.092. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20381473
-
Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of dendritic remodeling in hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons.J Neurosci. 2002 Aug 1;22(15):6810-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-15-06810.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12151561 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The TAAR1 Agonist PCC0105004 Regulates Amygdala Synaptic Plasticity to Alleviate Anxiety-Like Behaviors in Rats.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2025 Apr;13(2):e70068. doi: 10.1002/prp2.70068. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2025. PMID: 40186385 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid actions on synapses, circuits, and behavior: implications for the energetics of stress.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2014 Apr;35(2):180-196. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24361584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expression patterns in four brain areas associate with quantitative measure of estrous behavior in dairy cows.BMC Genomics. 2011 Apr 19;12:200. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-200. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21504592 Free PMC article.
-
Regional differences in acute corticosterone-induced dendritic remodeling in the rat brain and their behavioral consequences.BMC Neurosci. 2014 May 22;15:65. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-15-65. BMC Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24884833 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors produce rapid anti-anxiety responses through amygdala long-term depression in male rodents.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2017 Jun;42(4):230-241. doi: 10.1503/jpn.160116. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28234213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shelton CI. Diagnosis and management of anxiety disorders. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2004;104(3 Suppl 1):S2–5. - PubMed
-
- Shearer SL. Recent advances in the understanding and treatment of anxiety disorders. Prim Care. 2007;34(3):475–504. v–vi. - PubMed
-
- WHO . The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders-Diagnostic Criteria for Research. World Health Organization; Geneva: 1993.
-
- APA . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. fourth edition (DSM-IV) Washington DC: 1994.

