Keratinocytes as depository of ammonium-inducible glutamine synthetase: age- and anatomy-dependent distribution in human and rat skin
- PMID: 19204801
- PMCID: PMC2637544
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004416
Keratinocytes as depository of ammonium-inducible glutamine synthetase: age- and anatomy-dependent distribution in human and rat skin
Erratum in
- PLoS ONE. 2009;4(3). doi: 10.1371/annotation/fa1fbbb8-5dca-4afb-a5ee-c7eb3f5c45bc doi: 10.1371/annotation/fa1fbbb8-5dca-4afb-a5ee-c7eb3f5c45bc
Abstract
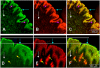
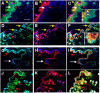
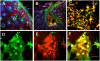
In inner organs, glutamine contributes to proliferation, detoxification and establishment of a mechanical barrier, i.e., functions essential for skin, as well. However, the age-dependent and regional peculiarities of distribution of glutamine synthetase (GS), an enzyme responsible for generation of glutamine, and factors regulating its enzymatic activity in mammalian skin remain undisclosed. To explore this, GS localization was investigated using immunohistochemistry and double-labeling of young and adult human and rat skin sections as well as skin cells in culture. In human and rat skin GS was almost completely co-localized with astrocyte-specific proteins (e.g. GFAP). While GS staining was pronounced in all layers of the epidermis of young human skin, staining was reduced and more differentiated among different layers with age. In stratum basale and in stratum spinosum GS was co-localized with the adherens junction component beta-catenin. Inhibition of, glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cultured keratinocytes and HaCaT cells, however, did not support a direct role of beta-catenin in regulation of GS. Enzymatic and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction studies revealed an unusual mode of regulation of this enzyme in keratinocytes, i.e., GS activity, but not expression, was enhanced about 8-10 fold when the cells were exposed to ammonium ions. Prominent posttranscriptional up-regulation of GS activity in keratinocytes by ammonium ions in conjunction with widespread distribution of GS immunoreactivity throughout the epidermis allows considering the skin as a large reservoir of latent GS. Such a depository of glutamine-generating enzyme seems essential for continuous renewal of epidermal permeability barrier and during pathological processes accompanied by hyperammonemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Chwals WJ. Regulation of the cellular and physiological effects of glutamine. Med Chem. 2004;4:833–838. - PubMed
-
- Gebhardt R, Mecke D. Cellular distribution and regulation of glutamine synthetase in liver. In: Häussinger D, Sies H, editors. Glutamate metabolism in mammalian tissues. Heidelberg: Springer Verlag; 1984. pp. 98–121.
-
- Gebhardt R, Gaunitz F, Mecke D. Heterogeneous (positional) expression of hepatic glutamine synthetase: features, regulation and implications for hepatocarcinogenesis. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1994;34:27–56. - PubMed
-
- Burch HB, Choi S, McCarthy WZ, Wong PY, Lowry OH. The location of glutamine synthetase within the rat and rabbit nephron. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978;82:498–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

