Growth factor-induced resistance to tamoxifen is associated with a mutation of estrogen receptor alpha and its phosphorylation at serine 305
- PMID: 19205871
- PMCID: PMC4482256
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-009-0334-0
Growth factor-induced resistance to tamoxifen is associated with a mutation of estrogen receptor alpha and its phosphorylation at serine 305
Abstract
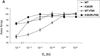
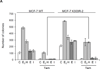
Estrogens play a crucial role in breast tumor growth, which is the rationale for the use of antiestrogens, such as tamoxifen, in women with estrogen receptor (ER)-alpha-positive breast cancer. However, hormone resistance is a major clinical problem. Altered growth factor signaling to the ERalpha pathway has been shown to be associated with the development of clinical resistance. We previously have identified a mutation that replaces arginine for lysine at residue 303 (K303R) of ERalpha, which confers hypersensitive growth in low levels of estrogen. To determine if the K303R mutation could participate in the evolution of hormone resistance, we generated MCF-7 breast cancer cells stably transfected with either wild-type (WT) or K303R ERalpha. We found that the mutation confers decreased sensitivity to tamoxifen in the presence of the growth factor heregulin, using anchorage-independent growth assays. K303R ERalpha-expressing cells were hypersensitive to growth factor signals. Our data suggest that phosphorylation of serine 305 within the hinge domain of ERalpha might play a key role in increasing ligand-independent activity of the mutant receptor. We hypothesize that the mutation adapts the receptor for enhanced bidirectional cross-talk with the HER2 growth factor receptor pathway, which then impacts on responsiveness to tamoxifen.
Figures

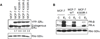
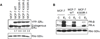
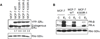
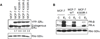
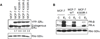

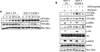
References
-
- O’Malley BW. Molecular biology. Little molecules with big goals. Science. 2006;313(5794):1749–1750. - PubMed
-
- Bjornstrom L, Sjoberg M. Mechanisms of estrogen receptor signaling: convergence of genomic and nongenomic actions on target genes. Mol Endocrinol. 2005;19(4):833–842. - PubMed
-
- Fuqua SAW, Wiltschke C, Zhang QX, Borg A, Castles CG, Friedrichs WE, Hopp T, Hilsenbeck S, Mohsin S, O’Connell P, Allred DC. A hypersensitive estrogen receptor-α mutation in premalignant breast lesions. Cancer Research. 2000;60(15):4026–4029. - PubMed
-
- Tebbit CL, Bentley RC, Olson JA, Jr, Marks JR. Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) mutant A908G is not a common feature in benign and malignant proliferations of the breast. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2004;40(1):51–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

