Biocompatible luminescent silicon quantum dots for imaging of cancer cells
- PMID: 19206483
- PMCID: PMC2676166
- DOI: 10.1021/nn700319z
Biocompatible luminescent silicon quantum dots for imaging of cancer cells
Abstract
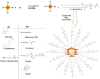
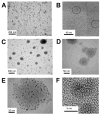
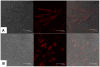
Luminescent silicon quantum dots (Si QDs) have great potential for use in biological imaging and diagnostic applications. To exploit this potential, they must remain luminescent and stably dispersed in water and biological fluids over a wide range of pH and salt concentration. There have been many challenges in creating such stable water-dispersible Si QDs, including instability of photoluminescence due their fast oxidation in aqueous environments and the difficulty of attaching hydrophilic molecules to Si QD surfaces. In this paper, we report the preparation of highly stable aqueous suspensions of Si QDs using phospholipid micelles, in which the optical properties of Si nanocrystals are retained. These luminescent micelle-encapsulated Si QDs were used as luminescent labels for pancreatic cancer cells. This paves the way for silicon quantum dots to be a valuable optical probe in biomedical diagnostics.
Figures

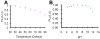
References
-
- Prasad PN. Nanophotonics. Wiley-Interscience; New York: 2004.
-
- Alivisatos AP. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science. 1996;271:933–937.
-
- Prasad PN. Introduction to Biophotonics. Wiley-Interscience; Hoboken, NJ: 2003.
-
- Gao X, Yang L, Petros JA, Marshall FF, Simons JW, Nie S. In vivo molecular and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 2005;16:63–72. - PubMed
-
- Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat Mater. 2005;4:435–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

