C-H bonds as ubiquitous functionality: a general approach to complex arylated pyrazoles via sequential regioselective C-arylation and N-alkylation enabled by SEM-group transposition
- PMID: 19206533
- PMCID: PMC2954770
- DOI: 10.1021/ja8096114
C-H bonds as ubiquitous functionality: a general approach to complex arylated pyrazoles via sequential regioselective C-arylation and N-alkylation enabled by SEM-group transposition
Abstract
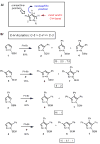
Pyrazoles are important azole heteroarenes frequently found in pharmaceuticals and protein ligands, and there has been a growing interest in new synthetic methods for their preparation. We report the first catalytic intermolecular C-H arylation of pyrazoles, namely SEM-protected pyrazoles and N-alkylpyrazoles, which lays the foundation for a new approach to the synthesis of complex arylated pyrazoles, where new arene rings are directly attached to predetermined positions of the heteroarene nucleus ("topologically obvious synthesis"). Through a systematic search, we identified a palladium-pivalate catalytic system as the most effective protocol and mapped the reactivity of all three C-H bonds of the pyrazole (C-5 > C-4 >> C-3). To circumvent the low reactivity of the C-3 position, we developed a "SEM switch", which transposes the SEM-protecting group from one nitrogen to the other in one step, and in the process transforms the unreactive C-3 position to the reactive C-5 position. The SEM switch thus enables sequential arylation of C-5 and C-3 position, providing rapid access to protected or free 3,4,5-triarylpyrazoles (the C-4 arene ring is readily introduced by bromination and Suzuki coupling). Furthermore, N-alkylation of SEM-protected pyrazoles allows for regioselective introduction of the amine substituent, addressing the low regioselectivity of N-alkylation of pyrazoles lacking sufficient steric bias. Thus, the catalytic C-H arylation combined with the protecting group transposition and N-alkylation provides a rapid route to fully substituted pyrazoles with complete regiocontrol of all substituents. The particular strength of this strategy is the ability to commence the synthesis from either the parent pyrazole or practically any pyrazole intermediate.
Figures

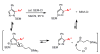

References
-
- Pozharskii AF, Soldatenkov AT, Katritzky AR. Heterocycles in Life and Society. Wiley; Chichester, NY: 1997.
-
- Elguero J. In: Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry. Katrizky AR, Rees CW, Scriven EFV, editors. Vol. 5 Pergamon; Oxford: 1996.
-
- Sliskovich DR, Roth BD, Wilson MW, Hoefle ML, Newton RS. J Med Chem. 1990;33:31–38. - PubMed
-
- Penning TD, Talley JJ, Bertenshaw SR, Carter JS, Collins PW, Docter S, Graneto MJ, Lee LF, Malecha JW, Miyashiro JM, Roger RS, Rogier DJ, Yu SS, Anderson GD, Burton EG, Cogburn JN, Gregory SA, Koboldt CM, Perkins WE, Seibert K, Veenhuizen AW, Zhang YY, Isakson PC. J Med Chem. 1997;40:1347–1365. - PubMed
-
- Stauffer SR, Katzenellenbogen JA. J Comb Chem. 2000;2:318–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

