Resveratrol amplifies profibrogenic effects of free fatty acids on human hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 19207580
- PMCID: PMC2893585
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2008.00485.x
Resveratrol amplifies profibrogenic effects of free fatty acids on human hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
Aim: To ascertain whether resveratrol affects the expression of free fatty acids (FFA)-induced profibrogenic genes, death receptors, and/or apoptosis-related molecules in human hepatic stellate cells, using the LX-2 cell line.
Methods: Cells were cultured in the presence of FFAs (2:1 oleate : palmitate) and subsequently treated with resveratrol. Gene expression rates were determined by quantitative real-time PCR. The 50% lethal dose (LD(50)) of resveratrol in the presence of FFAs was assessed with the MTT viability test.
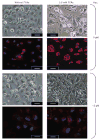
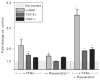
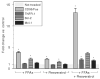
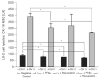
Results: Compared to vehicle controls, incubation of LX-2 cells with 0.5 mM FFAs induced profibrogenic genes (alpha-SMA x 2.9; TGF-beta1 x 1.6; TIMP-1 x 1.4), death receptors (CD95/Fas x 3.8; TNFR-1 x 1.4), and anti-apoptotic molecules (Bcl-2 x 2.3; Mcl-1 x 1.3). Subsequent addition of 15 microM resveratrol (LD(50) = 23.2 microM) significantly (P < 0.05) upregulated further these genes (alpha-SMA x 6.5; TGF-beta1 x 1.9; TIMP-1 x 2.2; CD95/Fas x 13.1, TNFR-1 x 2.1; Bcl-2 x 3.6; Mcl-1 x 1.9). Importantly, this effect was only observed in the presence of FFAs.
Conclusion: Resveratrol amplifies the profibrogenic activation of human hepatic LX-2 stellate cells. This finding raises the possibility that in obese patients with elevated FFAs reserveratrol could provoke hepatic fibrogenesis. In-vivo studies are necessary to further validate this conclusion.
Figures
References
-
- St leger AS, Cochrane AL, Moore F. Factors associated with cardiac mortality in developed countries with particular reference to the consumption of wine. Lancet. 1979;1 (8124):1017–20. - PubMed
-
- Sun AY, Simonyi A, Sun GY. The “French Paradox” and beyond: neuroprotective effects of polyphenols. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;32:314–18. - PubMed
-
- Shimada K, Watanabe H, Hosoda K, Takeuchi K, Yoshikawa J. Effect of red wine on coronary flow-velocity reserve. Lancet. 1999;354:1002. - PubMed
-
- van Velden DP, Mansvelt EP, Fourie E, Rossouw M, Marais AD. The cardioprotective effect of wine on human blood chemistry. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;957:337–40. - PubMed
-
- Frankel EN, Kanner J, German JB, et al. Inhibition of oxidation of human low-density lipoprotein by phenolic substances in red wine. Lancet. 1993;341:454–7. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

