Treatment with sirolimus results in complete responses in patients with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome
- PMID: 19208097
- PMCID: PMC2819393
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.07595.x
Treatment with sirolimus results in complete responses in patients with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome
Abstract
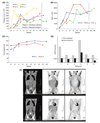
We hypothesized that sirolimus, an mTOR inhibitor, may be effective in patients with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) and treated patients who were intolerant to or failed other therapies. Four patients were treated for autoimmune cytopenias; all had a rapid complete or near complete response. Two patients were treated for autoimmune arthritis and colitis, demonstrating marked improvement. Three patients had complete resolution of lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly and all patients had a reduction in double negative T cells, a population hallmark of the disease. Based on these significant responses, we recommend that sirolimus be considered as second-line therapy for patients with steroid-refractory disease.
Conflict of interest statement
No author has competing financial interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Abdel-Karim IA, Giles FJ. Mammalian target of rapamycin as a target in hematological malignancies. Current Problems in Cancer. 2008;32:161–177. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia M, Stabilini A, Migliavacca B, Horejs-Hoeck J, Kaupper T, Roncarolo MG. Rapamycin promotes expansion of functional CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ regulatory T cells of both healthy subjects and type 1 diabetic patients. Journal of Immunology. 2006;177:8338–8347. - PubMed
-
- Bleesing JJ, Straus SE, Fleisher TA. Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. A human disorder of abnormal lymphocyte survival. Pediatric Clinics of North America. 2000;47:1291–1310. - PubMed
-
- Bleesing JJ, Brown MR, Straus SE, Dale JK, Siegel RM, Johnson M, Lenardo MJ, Puck JM, Fleisher TA. Immunophenotypic profiles in families with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. Blood. 2001;98:2466–2473. - PubMed
-
- Brusko TM, Putnam AL, Bluestone JA. Human regulatory T cells: role in autoimmune disease and therapeutic opportunities. Immunological Reviews. 2008;223:371–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

