PTP1B dephosphorylates N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor and elicits SNARE complex disassembly during human sperm exocytosis
- PMID: 19208619
- PMCID: PMC2667736
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M807614200
PTP1B dephosphorylates N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor and elicits SNARE complex disassembly during human sperm exocytosis
Abstract
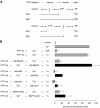
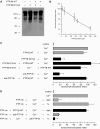
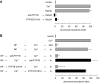
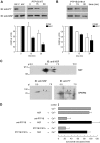
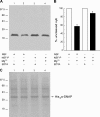
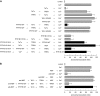
The reversible phosphorylation of tyrosyl residues in proteins is a cornerstone of the signaling pathways that regulate numerous cellular responses. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is controlled through the concerted actions of protein-tyrosine kinases and phosphatases. The goal of the present study was to unveil the mechanisms by which protein tyrosine dephosphorylation modulates secretion. The acrosome reaction, a specialized type of regulated exocytosis undergone by sperm, is initiated by calcium and carried out by a number of players, including tyrosine kinases and phosphatases, and fusion-related proteins such as Rab3A, alpha-SNAP, N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF), SNAREs, complexin, and synaptotagmin VI. We report here that inducers were unable to elicit the acrosome reaction when permeabilized human sperm were loaded with anti-PTP1B antibodies or with the dominant-negative mutant PTP1B D181A; subsequent introduction of wild type PTP1B or NSF rescued exocytosis. Wild type PTP1B, but not PTP1B D181A, caused cis SNARE complex dissociation during the acrosome reaction through a mechanism involving NSF. Unlike its non-phosphorylated counterpart, recombinant phospho-NSF failed to dissociate SNARE complexes from rat brain membranes. These results strengthen our previous observation that NSF activity is regulated rather than constitutive during sperm exocytosis and indicate that NSF must be dephosphorylated by PTP1B to disassemble SNARE complexes. Interestingly, phospho-NSF served as a substrate for PTP1B in an in vitro assay. Our findings demonstrate that phosphorylation of NSF on tyrosine residues prevents its SNARE complex dissociation activity and establish for the first time a role for PTP1B in the modulation of the membrane fusion machinery.
Figures
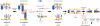
Similar articles
-
A connection between reversible tyrosine phosphorylation and SNARE complex disassembly activity of N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor unveiled by the phosphomimetic mutant N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor-Y83E.Mol Hum Reprod. 2019 Jul 1;25(7):344-358. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaz031. Mol Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 31194868
-
α-SNAP prevents docking of the acrosome during sperm exocytosis because it sequesters monomeric syntaxin.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021925. Epub 2011 Jul 18. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21789195 Free PMC article.
-
alpha-SNAP and NSF are required in a priming step during the human sperm acrosome reaction.Mol Hum Reprod. 2005 Jan;11(1):43-51. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gah126. Epub 2004 Nov 12. Mol Hum Reprod. 2005. PMID: 15542541
-
Acrosomal exocytosis, a special type of regulated secretion.IUBMB Life. 2007 Apr-May;59(4-5):286-92. doi: 10.1080/15216540701222872. IUBMB Life. 2007. PMID: 17505967 Review.
-
Fusion of membranes during the acrosome reaction: a tale of two SNAREs.Mol Reprod Dev. 2000 Dec;57(4):309-10. doi: 10.1002/1098-2795(200012)57:4<309::AID-MRD1>3.0.CO;2-W. Mol Reprod Dev. 2000. PMID: 11066058 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B impairs diabetic wound healing through vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 dephosphorylation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Jan;35(1):163-74. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304705. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25395617 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein is required for sperm exocytosis at a post-fusion stage.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 23;11:1125988. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1125988. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37287458 Free PMC article.
-
Epac, Rap and Rab3 act in concert to mobilize calcium from sperm's acrosome during exocytosis.Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Aug 27;12:43. doi: 10.1186/s12964-014-0043-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2014. PMID: 25159528 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-tyrosine kinase signaling in the biological functions associated with sperm.J Signal Transduct. 2012;2012:181560. doi: 10.1155/2012/181560. Epub 2012 Nov 11. J Signal Transduct. 2012. PMID: 23209895 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D1A directly interacts with otoferlin synaptic pathway proteins: Ca2+ and phosphorylation underlie an NSF-to-AP2mu1 molecular switch.Biochem J. 2017 Jan 1;474(1):79-104. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160690. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 27821621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burgoyne, R. D., and Morgan, A. (2003) Physiol. Rev. 83 581–632 - PubMed
-
- Sollner, T. H. (2003) Mol. Membr. Biol. 20 209–220 - PubMed
-
- Jahn, R., Lang, T., and Sudhof, T. C. (2003) Cell 112 519–533 - PubMed
-
- Jahn, R., and Scheller, R. H. (2006) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7 631–643 - PubMed
-
- Sutton, R. B., Fasshauer, D., Jahn, R., and Brunger, A. T. (1998) Nature 395 347–353 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

