Characterization of a selective inhibitor of inositol hexakisphosphate kinases: use in defining biological roles and metabolic relationships of inositol pyrophosphates
- PMID: 19208622
- PMCID: PMC2667744
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M900752200
Characterization of a selective inhibitor of inositol hexakisphosphate kinases: use in defining biological roles and metabolic relationships of inositol pyrophosphates
Abstract
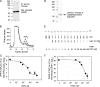
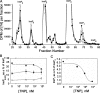
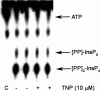
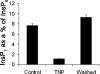
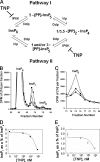
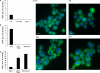
Inositol hexakisphosphate kinases (IP6Ks) phosphorylate inositol hexakisphosphate (InsP(6)) to yield 5-diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate (5-[PP]-InsP(5) or InsP(7)). In this study, we report the characterization of a selective inhibitor, N(2)-(m-(trifluoromethy)lbenzyl) N(6)-(p-nitrobenzyl)purine (TNP), for these enzymes. TNP dose-dependently and selectively inhibited the activity of IP6K in vitro and inhibited InsP(7) and InsP(8) synthesis in vivo without affecting levels of other inositol phosphates. TNP did not inhibit either human or yeast Vip/PPIP5K, a newly described InsP(6)/InsP(7) 1/3-kinase. Overexpression of IP6K1, -2, or -3 in cells rescued TNP inhibition of InsP(7) synthesis. TNP had no effect on the activity of a large number of protein kinases, suggesting that it is selective for IP6Ks. TNP reversibly reduced InsP(7)/InsP(8) levels. TNP in combination with genetic studies was used to implicate the involvement of two pathways for synthesis of InsP(8) in yeast. TNP induced a fragmented vacuole phenotype in yeast, consistent with inhibition of Kcs1, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae IP6K. In addition, it also inhibited insulin release from Min6 cells in a dose-dependent manner further implicating InsP(7) in this process. TNP thus provides a means of selectively and rapidly modulating cellular InsP(7) levels, providing a new and versatile tool to study the biological function and metabolic relationships of inositol pyrophosphates.
Figures

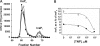
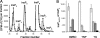
References
-
- Luo, H. R., Huang, Y. E., Chen, J. C., Saiardi, A., Iijima, M., Ye, K., Huang, Y., Nagata, E., Devreotes, P., and Snyder, S. H. (2003) Cell 114 559-572 - PubMed
-
- Saiardi, A., Caffrey, J. J., Snyder, S. H., and Shears, S. B. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275 24686-24692 - PubMed
-
- Saiardi, A., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Snowman, A. M., Tempst, P., and Snyder, S. H. (1999) Curr. Biol. 9 1323-1326 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

