Epigenetics meets estrogen receptor: regulation of estrogen receptor by direct lysine methylation
- PMID: 19208734
- PMCID: PMC3901989
- DOI: 10.1677/ERC-08-0305
Epigenetics meets estrogen receptor: regulation of estrogen receptor by direct lysine methylation
Abstract
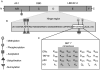
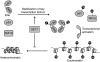
The nuclear hormone receptor estrogen receptor α (ERα) promotes cellular growth through ligand-dependent activation of specific target genes, a process which is targeted in the treatment of ERα-expressing breast cancers. ERα activity is regulated at the protein level by post-translational modifications including phosphorylation and acetylation. A study now shows that ERα can also be directly methylated at lysine 302 (K302) by SET7, a histone methyltransferase that is known to monomethylate H3K4 and is associated with transcriptional activation. It was shown that K302 methylation stabilizes ERα protein and is suggested to increase sensitivity of ERα to estrogens, enhancing transcription of estrogen response elements. Furthermore, SET7 methylation of K302 is enhanced by a breast cancer-associated mutation at K303 (K303R) in vitro. These findings provide an additional mechanism of SET7 mediated transcriptional activation, as well as potential insight into the complex regulation of ERα stability and ligand sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of estrogen receptor alpha by the SET7 lysine methyltransferase.Mol Cell. 2008 May 9;30(3):336-47. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.03.022. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18471979 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into estrogen receptor α methylation by histone methyltransferase SMYD2, a cellular event implicated in estrogen signaling regulation.J Mol Biol. 2014 Oct 9;426(20):3413-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.02.019. Epub 2014 Mar 1. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24594358
-
Epigenetics and beyond: targeting writers of protein lysine methylation to treat disease.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021 Apr;20(4):265-286. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-00108-x. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 33469207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone H3 lysine 9 methyltransferase G9a is a transcriptional coactivator for nuclear receptors.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 31;281(13):8476-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511093200. Epub 2006 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16461774 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics in development.Dev Dyn. 2007 Apr;236(4):1144-56. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21094. Dev Dyn. 2007. PMID: 17304537 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics addressing the estrogen receptor subtype-mediated effects in T47D breast cancer cells exposed to the phytoestrogen genistein.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Jan;10(1):M110.002170. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M110.002170. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 20884965 Free PMC article.
-
Selective mutations in estrogen receptor alpha D-domain alters nuclear translocation and non-estrogen response element gene regulatory mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 8;286(14):12640-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.187773. Epub 2011 Feb 1. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21285458 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of ERα signaling differentially modulates IFN-γ induced HLA-class II expression in breast cancer cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e87377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087377. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475282 Free PMC article.
-
Liganded and unliganded activation of estrogen receptor and hormone replacement therapies.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Aug;1812(8):1054-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.05.001. Epub 2011 May 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21605666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen- and Progesterone (P4)-Mediated Epigenetic Modifications of Endometrial Stromal Cells (EnSCs) and/or Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells (MSCs) in the Etiopathogenesis of Endometriosis.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021 Aug;17(4):1174-1193. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-10115-5. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021. PMID: 33411206 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chuikov S, Kurash JK, Wilson JR, Xiao B, Justin N, Ivanov GS, McKinney K, Tempst P, Prives C, Gamblin SJ, Barlev NA, Reinberg D. Regulation of p53 activity through lysine methylation. Nature. 2004;432:353–360. - PubMed
-
- Conway K, Parrish E, Edmiston SN, Tolbert D, Tse CK, Geradts J, Livasy CA, Singh H, Newman B, Millikan RC. The estrogen receptor-alpha A908G (K303R) mutation occurs at a low frequency in invasive breast tumors: results from a population-based study. Breast Cancer Research. 2005;7:871–880. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Couture JF, Collazo E, Hauk G, Trievel RC. Structural basis for the methylation site specificity of SET7/9. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology. 2006;13:140–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

