Interleukin-21 is required for the development of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice
- PMID: 19208913
- PMCID: PMC2671036
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-0882
Interleukin-21 is required for the development of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice
Abstract
Objective: Interleukin (IL)-21 is a type 1 cytokine that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes via the unique biology of the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse strain. The aim of this study was to investigate a causal role for IL-21 in type 1 diabetes.
Research design and methods: We generated IL-21R-deficient NOD mice and C57Bl/6 mice expressing IL-21 in pancreatic beta-cells, allowing the determination of the role of insufficient and excessive IL-21 signaling in type 1 diabetes.
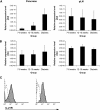
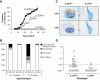
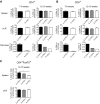
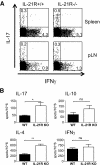
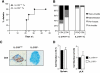
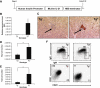
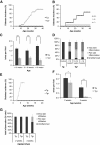
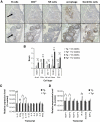
Results: Deficiency in IL-21R expression renders NOD mice resistant to insulitis, production of insulin autoantibodies, and onset of type 1 diabetes. The lymphoid compartment in IL-21R-/- NOD is normal and does not contain an increased regulatory T-cell fraction or diminished effector cytokine responses. However, we observed a clear defect in autoreactive effector T-cells in IL-21R-/- NOD by transfer experiments. Conversely, overexpression of IL-21 in pancreatic beta-cells induced inflammatory cytokine and chemokines, including IL-17A, IL17F, IFN-gamma, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1, MCP-2, and interferon-inducible protein-10 in the pancreas. The ensuing leukocytic infiltration in the islets resulted in destruction of beta-cells and spontaneous type 1 diabetes in the normally diabetes-resistant C57Bl/6 and NOD x C57Bl/6 backgrounds.
Conclusions: This work provides demonstration of the essential prodiabetogenic activities of IL-21 on diverse genetic backgrounds (NOD and C57BL/6) and indicates that IL-21 blockade could be a promising strategy for interventions in human type 1 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-21 regulates SOCS1 expression in autoreactive CD8+ T cells but is not required for acquisition of CTL activity in the islets of non-obese diabetic mice.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 25;9(1):15302. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51636-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31653894 Free PMC article.
-
IL-12 administration accelerates autoimmune diabetes in both wild-type and IFN-gamma-deficient nonobese diabetic mice, revealing pathogenic and protective effects of IL-12-induced IFN-gamma.J Immunol. 2003 Jun 1;170(11):5491-501. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.11.5491. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12759426
-
Islet-specific expression of IL-10 promotes diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice independent of Fas, perforin, TNF receptor-1, and TNF receptor-2 molecules.J Immunol. 2000 Sep 1;165(5):2841-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.5.2841. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10946317
-
IL-1 receptor deficiency slows progression to diabetes in the NOD mouse.Diabetes. 2004 Jan;53(1):113-21. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.1.113. Diabetes. 2004. PMID: 14693705
-
An update on cytokines in the pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Metab Rev. 1998 Jun;14(2):129-51. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-0895(199806)14:2<129::aid-dmr208>3.0.co;2-v. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1998. PMID: 9679667 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenic mechanisms in type 1 diabetes: the islet is both target and driver of disease.Rev Diabet Stud. 2012 Winter;9(4):148-68. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2012.9.148. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Rev Diabet Stud. 2012. PMID: 23804258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymic B Cell-Mediated Attack of Thymic Stroma Precedes Type 1 Diabetes Development.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 7;9:1281. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01281. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29930554 Free PMC article.
-
The circadian gene Arntl2 on distal mouse chromosome 6 controls thymocyte apoptosis.Mamm Genome. 2017 Feb;28(1-2):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s00335-016-9665-4. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Mamm Genome. 2017. PMID: 27671790
-
Interleukin-21 receptor-mediated signals control autoreactive T cell infiltration in pancreatic islets.Immunity. 2012 Jun 29;36(6):1060-72. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.04.005. Epub 2012 May 10. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22579473 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of T Cell Receptor Signaling in the Development of Type 1 Diabetes.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 2;11:615371. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.615371. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33603744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson MS, Bluestone JA: The NOD mouse: a model of immune dysregulation. Annu Rev Immunol 2005; 23: 447– 385 - PubMed
-
- Wicker LS, Todd JA, Peterson LB: Genetic control of autoimmune diabetes in the NOD mouse. Annu Rev Immunol 1995; 13: 179– 200 - PubMed
-
- King C, Ilic A, Koelsch K, Sarvetnick N: Homeostatic expansion of T cells during immune insufficiency generates autoimmunity. Cell 2004; 117: 265– 277 - PubMed
-
- Mehta DS, Wurster AL, Grusby MJ: Biology of IL-21 and the IL-21 receptor. Immunol Rev 2004; 202: 84– 95 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

