Whole-motion model of perception during forward- and backward-facing centrifuge runs
- PMID: 19208962
- PMCID: PMC2775489
Whole-motion model of perception during forward- and backward-facing centrifuge runs
Abstract
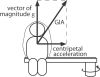
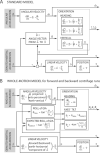
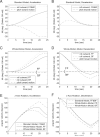
Illusory perceptions of motion and orientation arise during human centrifuge runs without vision. Asymmetries have been found between acceleration and deceleration, and between forward-facing and backward-facing runs. Perceived roll tilt has been studied extensively during upright fixed-carriage centrifuge runs, and other components have been studied to a lesser extent. Certain, but not all, perceptual asymmetries in acceleration-vs-deceleration and forward-vs-backward motion can be explained by existing analyses. The immediate acceleration-deceleration roll-tilt asymmetry can be explained by the three-dimensional physics of the external stimulus; in addition, longer-term data has been modeled in a standard way using physiological time constants. However, the standard modeling approach is shown in the present research to predict forward-vs-backward-facing symmetry in perceived roll tilt, contradicting experimental data, and to predict perceived sideways motion, rather than forward or backward motion, around a curve. The present work develops a different whole-motion-based model taking into account the three-dimensional form of perceived motion and orientation. This model predicts perceived forward or backward motion around a curve, and predicts additional asymmetries such as the forward-backward difference in roll tilt. This model is based upon many of the same principles as the standard model, but includes an additional concept of familiarity of motions as a whole.
Figures
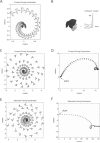
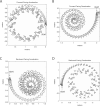
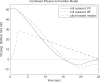
Similar articles
-
Baselines for three-dimensional perception of combined linear and angular self-motion with changing rotational axis.J Vestib Res. 2000;10(4-5):163-78. J Vestib Res. 2000. PMID: 11354430
-
Three-dimensional baselines for perceived self-motion during acceleration and deceleration in a centrifuge.J Vestib Res. 1997 Jan-Feb;7(1):45-61. J Vestib Res. 1997. PMID: 9057159
-
Spatial disorientation in gondola centrifuges predicted by the form of motion as a whole in 3-D.Aviat Space Environ Med. 2009 Feb;80(2):125-34. doi: 10.3357/asem.2344.2009. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2009. PMID: 19198199 Free PMC article.
-
The perception of roll tilt in pilots during a simulated coordinated turn in a gondola centrifuge.Aviat Space Environ Med. 2011 May;82(5):523-30. doi: 10.3357/asem.2898.2011. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2011. PMID: 21614866
-
Perception of motion and position relative to the earth. An overview.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 May 22;656:315-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb25218.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992. PMID: 1599152 Review.
Cited by
-
Neck stabilization through sensory integration of vestibular and visual motion cues.Front Neurol. 2023 Nov 23;14:1266345. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1266345. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38073639 Free PMC article.
-
Head position modulates optokinetic nystagmus.Exp Brain Res. 2011 Aug;213(1):141-52. doi: 10.1007/s00221-011-2785-x. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Exp Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21735244 Free PMC article.
-
The time constant of the somatogravic illusion.Exp Brain Res. 2013 Feb;224(3):313-21. doi: 10.1007/s00221-012-3313-3. Epub 2012 Nov 4. Exp Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23124839
-
Asymmetries and three-dimensional features of vestibular cross-coupled stimuli illuminated through modeling.J Vestib Res. 2016 Nov 3;26(4):343-358. doi: 10.3233/VES-160585. J Vestib Res. 2016. PMID: 27814310 Free PMC article.
-
Differences between perception and eye movements during complex motions.J Vestib Res. 2011;21(4):193-208. doi: 10.3233/VES-2011-0416. J Vestib Res. 2011. PMID: 21846952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angelaki DE, Shaikh AG, Green AM, Dickman JD. Neurons compute internal models of the physical laws of motion. Nature. 2004;430:560–564. - PubMed
-
- Bertin RJV, Israël I. Optic-flow-based perception of two-dimensional trajectories and the effects of a single landmark. Perception. 2005;34:453–475. - PubMed
-
- Bertin RJV, Israël I, Lappe M. Perception of two-dimensional, simulated ego-motion trajectories from optic flow. Vision Research. 2000;40:2951–2971. - PubMed
-
- Bockisch CJ, Straumann D, Haslwanter T. Eye movements during multi-axis whole-body rotations. J Neurophysiol. 2003;89:355–366. - PubMed
-
- Boring EG, Langfeld HS, Weld HP. Foundations of Psychology. John Wiley and Sons, Inc.; New York: 1948.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
