Risk stratification for arrhythmic death in an emergency department cohort: a new method of nonlinear PD2i analysis of the ECG
- PMID: 19209249
- PMCID: PMC2621378
- DOI: 10.2147/tcrm.s2741
Risk stratification for arrhythmic death in an emergency department cohort: a new method of nonlinear PD2i analysis of the ECG
Abstract
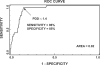
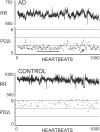
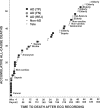
Heart rate variability (HRV) reflects both cardiac autonomic function and risk of sudden arrhythmic death (AD). Indices of HRV based on linear stochastic models are independent risk factors for AD in postmyocardial infarction (MI) cohorts. Indices based on nonlinear deterministic models have a higher sensitivity and specificity for predicting AD in retrospective data. A new nonlinear deterministic model, the automated Point Correlation Dimension (PD2i), was prospectively evaluated for prediction of AD. Patients were enrolled (N = 918) in 6 emergency departments (EDs) upon presentation with chest pain and being determined to be at risk of acute MI (AMI) >7%. Brief digital ECGs (>1000 heartbeats, approximately 15 min) were recorded and automated PD2i results obtained. Out-of-hospital AD was determined by modified Hinkle-Thaler criteria. All-cause mortality at 1 year was 6.2%, with 3.5% being ADs. Of the AD fatalities, 34% were without previous history of MI or diagnosis of AMI. The PD2i prediction of AD had sensitivity = 96%, specificity = 85%, negative predictive value = 99%, and relative risk >24.2 (p ≤ 0.001). HRV analysis by the time-dependent nonlinear PD2i algorithm can accurately predict risk of AD in an ED cohort and may have both life-saving and resource-saving implications for individual risk assessment.
Keywords: chaos; heart rate variability; non-linear; sudden death; ventricular arrhythmias.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of linear-stochastic and nonlinear-deterministic algorithms in the analysis of 15-minute clinical ECGs to predict risk of arrhythmic death.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009 Jun;5(3):671-82. doi: 10.2147/tcrm.s5568. Epub 2009 Aug 20. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009. PMID: 19707283 Free PMC article.
-
Nonlinear analysis of the heartbeats in public patient ECGs using an automated PD2i algorithm for risk stratification of arrhythmic death.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2008 Apr;4(2):549-57. doi: 10.2147/tcrm.s2521. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2008. PMID: 18728829 Free PMC article.
-
Heart rate variability in the human transplanted heart: nonlinear dynamics and QT vs RR-QT alterations during exercise suggest a return of neurocardiac regulation in long-term recovery.Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 1996 Oct-Dec;31(4):289-305. doi: 10.1007/BF02691433. Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 1996. PMID: 8982761
-
Use of left ventricular ejection fraction or wall-motion score index in predicting arrhythmic death in patients following an acute myocardial infarction. The TRACE Study Group.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1997 Oct;20(10 Pt 2):2553-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1997.tb06104.x. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9358502 Review.
-
Serum markers in the emergency department diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2001 May;19(2):321-37. doi: 10.1016/s0733-8627(05)70186-3. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2001. PMID: 11373981 Review.
Cited by
-
Prediction of Sudden Cardiac Death Risk with a Support Vector Machine Based on Heart Rate Variability and Heartprint Indices.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Sep 25;20(19):5483. doi: 10.3390/s20195483. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32992675 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of linear-stochastic and nonlinear-deterministic algorithms in the analysis of 15-minute clinical ECGs to predict risk of arrhythmic death.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009 Jun;5(3):671-82. doi: 10.2147/tcrm.s5568. Epub 2009 Aug 20. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009. PMID: 19707283 Free PMC article.
-
Heart rate variability biofeedback: how and why does it work?Front Psychol. 2014 Jul 21;5:756. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00756. eCollection 2014. Front Psychol. 2014. PMID: 25101026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akselrod S, Gordon D, Ubel FA, et al. Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuation: a quantitative probe of beat to beat cardiovascular control. Science. 1981;213:220–2. - PubMed
-
- Beaglehole R, Stewart AW, Butler M. Comparability of old and new World Health Organization criteria for definite myocardial infarction. Intl J Epidemiol. 1987;16:373–6. - PubMed
-
- Bigger JT, Jr, Whang W, Rottman JN, et al. Mechanisms of death in the CABG Patch trial: a randomized trial of implantable cardiac defibrillator prophylaxis in patients at high risk of death after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Circulation. 1999;99:1416–21. - PubMed
-
- Braun C, Kowallik P, Freking A, et al. Demonstration of nonlinear components in heart rate variability of healthy persons. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:H1577–84. - PubMed
-
- Carpeggiani C, Landisman C, Montaron M-F, et al. Cryoblockade in limbic brain (amygdala) delays or prevents ventricular fibrillation following coronary artery occlusion in psychologically stressed pigs. Circ Res. 1992;70:600–6. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

