Microfluidic device for multimodal characterization of pancreatic islets
- PMID: 19209341
- PMCID: PMC3759253
- DOI: 10.1039/b809590f
Microfluidic device for multimodal characterization of pancreatic islets
Abstract
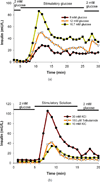
A microfluidic device to perfuse pancreatic islets while simultaneously characterizing their functionality through fluorescence imaging of the mitochondrial membrane potential and intracellular calcium ([Ca(2+)](i)) in addition to enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) quantification of secreted insulin was developed and characterized. This multimodal characterization of islet function will facilitate rapid assessment of tissue quality immediately following isolation from donor pancreas and allow more informed transplantation decisions to be made which may improve transplantation outcomes. The microfluidic perfusion chamber allows flow rates of up to 1 mL min(-1), without any noticeable perturbation or shear of islets. This multimodal quantification was done on both mouse and human islets. The ability of this simple microfluidic device to detect subtle variations in islet responses in different functional assays performed in short time-periods demonstrates that the microfluidic perfusion chamber device can be used as a new gold standard to perform comprehensive islet analysis and obtain a more meaningful predictive value for islet functionality prior to transplantation into recipients, which is currently difficult to predict using a single functional assay.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Microfluidic perifusion and imaging device for multi-parametric islet function assessment.Biomed Microdevices. 2010 Jun;12(3):409-17. doi: 10.1007/s10544-010-9398-1. Biomed Microdevices. 2010. PMID: 20300858
-
Islet preconditioning via multimodal microfluidic modulation of intermittent hypoxia.Anal Chem. 2012 Feb 21;84(4):1987-93. doi: 10.1021/ac2030909. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22296179 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic prevention of bubble formation and accumulation for long-term culture of pancreatic islet cells in microfluidic device.Biomed Microdevices. 2012 Apr;14(2):419-26. doi: 10.1007/s10544-011-9618-3. Biomed Microdevices. 2012. PMID: 22252566 Free PMC article.
-
A microfluidic device designed to induce media flow throughout pancreatic islets while limiting shear-induced damage.Lab Chip. 2013 Nov 21;13(22):4374-84. doi: 10.1039/c3lc50680k. Lab Chip. 2013. PMID: 24056576
-
A microfluidic system for monitoring glucagon secretion from human pancreatic islets of Langerhans.Anal Methods. 2021 Aug 28;13(32):3614-3619. doi: 10.1039/d1ay00703c. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Anal Methods. 2021. PMID: 34308945 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Functional differences between aggregated and dispersed insulin-producing cells.Diabetologia. 2013 Jul;56(7):1557-68. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2903-3. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Diabetologia. 2013. PMID: 23604550 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative and temporal control of oxygen microenvironment at the single islet level.J Vis Exp. 2013 Nov 17;(81):e50616. doi: 10.3791/50616. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 24299958 Free PMC article.
-
Islet assessment for transplantation.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2009 Dec;14(6):674-82. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e328332a489. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19812494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring hormone and small molecule secretion dynamics from islets-on-chip.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Feb;415(4):533-544. doi: 10.1007/s00216-022-04460-2. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 36459167 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered tools to study endocrine dysfunction of pancreas.Biophys Rev (Melville). 2024 Oct 22;5(4):041303. doi: 10.1063/5.0220396. eCollection 2024 Dec. Biophys Rev (Melville). 2024. PMID: 39449867 Review.
References
-
- Okubo Y, Shimada A, Kanazawa Y, Shigihara T, Oikawa Y, Imai T, Miyazaki J, Itoh H. Hyperplastic islets observed in "reversed" NOD mice treated without hematopoietic cells. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;79(1):18–23. - PubMed
-
- Keymeulen B, Vandemeulebroucke E, Ziegler AG, Mathieu C, Kaufman L, Hale G, Gorus F, Goldman M, Walter M, Candon S, Schandene L, Crenier L, De Block C, Seigneurin JM, De Pauw P, Pierard D, Weets I, Rebello P, Bird P, Berrie E, Frewin M, Waldmann H, Bach JF, Pipeleers D, Chatenoud L. Insulin needs after CD3-antibody therapy in new-onset type 1 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;352(25):2598–2608. - PubMed
-
- Lin JM, Sternesjo J, Sandler S, Bergsten P. Preserved pulsatile insulin release from prediabetic mouse islets. Endocrinology. 1999;140(9):3999–4004. - PubMed
-
- Lin JM, Fabregat ME, Gomis R, Bergsten P. Pulsatile insulin release from islets isolated from three subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51(4):988–993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

