Staff engagement during complex pediatric medical care: the role of patient, family, and treatment variables
- PMID: 19209401
- PMCID: PMC2775508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pec.2008.07.051
Staff engagement during complex pediatric medical care: the role of patient, family, and treatment variables
Abstract
Objective: To examine the role of patient, family, and treatment variables on self-reported engagement for physicians and nurses working with pediatric complex care patients.
Methods: Sixty-eight physicians and 85 registered nurses at a children's hospital reviewed eight case scenarios that varied by the patient and patient's family (each cooperative versus difficult) and the length of hospitalization (<30 days versus >30 days). Participants rated their engagement from highly engaged/responsive to distancing/disconnected behaviors.
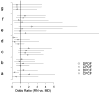
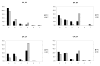
Results: Nurses were more likely than physicians to engage in situations with a difficult patient/cooperative family but less likely to engage in situations with a cooperative patient/difficult family.Nurses were more likely to consult a colleague regarding the care of a difficult patient/difficult family,while physicians were more likely to refer a difficult patient/difficult family to a psychosocial professional.
Conclusions: Differences were found for engagement with "difficult" patients/families, with physicians more likely to distance themselves or refer to a psychosocial professional, while nurses were more likely to consult with a colleague.
Practice implications: Communication between health care team members is essential for optimal family-centered health care. Thus, interventions are needed that focus on communication and support for healthcare teams working with pediatric complex care patients and their families.
Figures
References
-
- Sieben-Hein D, Steinmiller EA. Working with complex care patients. J Pediatr Nurs. 2005;20:389–95. - PubMed
-
- Haas LJ, Leiser JP, Magill MK, Sanyer ON. Management of the difficult patient. Am Fam Physician. 2005;72:2063–8. - PubMed
-
- Kazak AE, Rourke MT, Alderfer MA, Pai A, Reilly AF, Meadows AT. Evidence-based assessment, intervention and psychosocial care in pediatric oncology: a blueprint for comprehensive services across treatment. J Pediatr Psychol. 2007;32:1099–110. - PubMed
-
- Tracy MF, Ceronsky C. Creating a collaborative environment to care for complex patients and families. AACN Clin Issues. 2001;12:383–400. - PubMed
-
- Sheldon LK, Barrett R, Ellington L. Difficult communication in nursing. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2006;38:41–7. - PubMed

