Genetic and vascular modifiers of age-sensitive cognitive skills: effects of COMT, BDNF, ApoE, and hypertension
- PMID: 19210038
- PMCID: PMC2729285
- DOI: 10.1037/a0013487
Genetic and vascular modifiers of age-sensitive cognitive skills: effects of COMT, BDNF, ApoE, and hypertension
Abstract
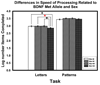
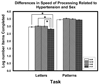
Several single nucleotide polymorphisms have been linked to neural and cognitive variation in healthy adults. We examined contribution of three polymorphisms frequently associated with individual differences in cognition (Catechol-O-Methyl-Transferase Val158Met, Brain-Derived-Neurotrophic-Factor Val66Met, and Apolipoprotein E epsilon4) and a vascular risk factor (hypertension) in a sample of 189 volunteers (age 18-82). Genotypes were determined from buccal culture samples, and cognitive performance was assessed in 4 age-sensitive domains?fluid intelligence, executive function (inhibition), associative memory, and processing speed. We found that younger age and COMT Met/Met genotype, associated with low COMT activity and higher prefrontal dopamine content, were independently linked to better performance in most of the tested domains. Homozygotes for Val allele of BDNF polymorphism exhibited better associative memory and faster speed of processing than the Met allele carriers, with greater effect for women and persons with hypertension. Carriers of ApoE epsilon4 allele evidenced steeper age-related increase in costs of Stroop color interference, but showed no negative effects on memory. The findings indicate that age-related cognitive performance is differentially affected by distinct genetic factors and their interactions with vascular health status.
(c) 2009 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cognitive ability, intraindividual variability, and common genetic variants of catechol-O-methyltransferase and brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a longitudinal study in a population-based sample of older adults.Psychol Aging. 2014 Jun;29(2):393-403. doi: 10.1037/a0035702. Psychol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24956006
-
Executive function performance and change in aging is predicted by apolipoprotein E, intensified by catechol-O-methyltransferase and brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and moderated by age and lifestyle.Neurobiol Aging. 2017 Apr;52:81-89. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.12.022. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Neurobiol Aging. 2017. PMID: 28131014 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of COMT, DRD2, BDNF, and APOE Genotypic Variation on Treatment Efficacy and Cognitive Side Effects of Electroconvulsive Therapy.J ECT. 2015 Jun;31(2):129-35. doi: 10.1097/YCT.0000000000000170. J ECT. 2015. PMID: 25148110
-
COMT Val158Met Genotype and Individual Differences in Executive Function in Healthy Adults.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2011 Jan;17(1):174-80. doi: 10.1017/S1355617710001402. Epub 2010 Dec 10. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2011. PMID: 21144101 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphisms for BDNF, COMT, and APOE do not affect gait or ankle motor control in chronic stroke: A preliminary cross-sectional study.Top Stroke Rehabil. 2021 Jan;28(1):72-80. doi: 10.1080/10749357.2020.1762060. Epub 2020 May 7. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 32378476 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lack of an association of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and plasma BDNF with hippocampal volume and memory.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2015 Sep;15(3):625-43. doi: 10.3758/s13415-015-0343-x. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25784293 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Modulated Associations between KIBRA, Brain Volume, and Verbal Memory among Healthy Older Adults.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Jan 10;9:431. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00431. eCollection 2017. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29375362 Free PMC article.
-
Age differences in arterial and venous extra-cerebral blood flow in healthy adults: contributions of vascular risk factors and genetic variants.Brain Struct Funct. 2017 Aug;222(6):2641-2653. doi: 10.1007/s00429-016-1362-2. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. PMID: 28120105 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical thickness mediates the relationship between DRD2 C957T polymorphism and executive function across the adult lifespan.Brain Struct Funct. 2021 Jan;226(1):121-136. doi: 10.1007/s00429-020-02169-5. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Brain Struct Funct. 2021. PMID: 33179159 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern of normal age-related regional differences in white matter microstructure is modified by vascular risk.Brain Res. 2009 Nov 10;1297:41-56. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.08.058. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19712671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander DM, Williams LM, Gatt JM, Dobson-Stone C, Kuan SA, Todd EG, Schofield PR, Cooper NJ, Gordon E. The contribution of apolipoprotein E alleles on cognitive performance and dynamic neural activity over six decades. Biological Psychology. 2007;75:229–238. - PubMed
-
- American Heart Association . Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics – 2005 Update. Dallas, TX: American Heart Association; 2004.
-
- Ando J, Ono Y, Wright MJ. Genetic structure of spatial and verbal working memory. Behavioral Genetics. 2001;31:615–624. - PubMed
-
- Bäckman L, Nyberg L, Lindenberger U, Li S-C, Farde L. The correlative triad among aging, dopamine, and cognition: current status and future prospects. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 2006;30:791–807. - PubMed
-
- Barnett JH, Jones PB, Robbins TW, Müller U. Effects of the catechol-O-methyltransferase Val158Met polymorphism on executive function: a meta-analysis of the Wisconsin Card Sort Test in schizophrenia and healthy controls. Molecular Psychiatry. 2007;12:502–509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

