Memory systems do not divide on consciousness: Reinterpreting memory in terms of activation and binding
- PMID: 19210052
- PMCID: PMC2747326
- DOI: 10.1037/a0013974
Memory systems do not divide on consciousness: Reinterpreting memory in terms of activation and binding
Abstract
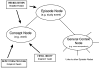
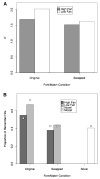
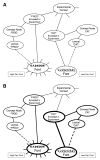
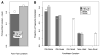
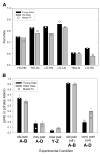
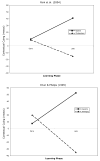
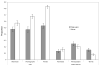
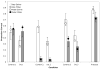
There is a popular hypothesis that performance on implicit and explicit memory tasks reflects 2 distinct memory systems. Explicit memory is said to store those experiences that can be consciously recollected, and implicit memory is said to store experiences and affect subsequent behavior but to be unavailable to conscious awareness. Although this division based on awareness is a useful taxonomy for memory tasks, the authors review the evidence that the unconscious character of implicit memory does not necessitate that it be treated as a separate system of human memory. They also argue that some implicit and explicit memory tasks share the same memory representations and that the important distinction is whether the task (implicit or explicit) requires the formation of a new association. The authors review and critique dissociations from the behavioral, amnesia, and neuroimaging literatures that have been advanced in support of separate explicit and implicit memory systems by highlighting contradictory evidence and by illustrating how the data can be accounted for using a simple computational memory model that assumes the same memory representation for those disparate tasks.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Memory and consciousness: a selective review of issues and data.Neuropsychologia. 1995 Sep;33(9):1131-41. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(95)00053-6. Neuropsychologia. 1995. PMID: 7501134 Review.
-
The porous boundaries between explicit and implicit memory: behavioral and neural evidence.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Apr;1224:174-190. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05946.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 21486300 Review.
-
Implicit memory. Retention without remembering.Am Psychol. 1990 Sep;45(9):1043-56. doi: 10.1037//0003-066x.45.9.1043. Am Psychol. 1990. PMID: 2221571 Review.
-
Implicit knowledge: new perspectives on unconscious processes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11113-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11113. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. PMID: 1454787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired implicit memory for gist information in amnesia.Neuropsychology. 2005 Nov;19(6):760-9. doi: 10.1037/0894-4105.19.6.760. Neuropsychology. 2005. PMID: 16351351
Cited by
-
Identical versus conceptual repetition FN400 and parietal old/new ERP components occur during encoding and predict subsequent memory.Brain Res. 2013 May 28;1512:68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.03.014. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23528265 Free PMC article.
-
Intact implicit verbal relational memory in medial temporal lobe amnesia.Neuropsychologia. 2012 Jul;50(8):2100-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.05.011. Epub 2012 May 17. Neuropsychologia. 2012. PMID: 22609574 Free PMC article.
-
Episodic memory without autonoetic consciousness.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024 Nov 4;379(1913):20230410. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0410. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39278243
-
Time to go our separate ways: opposite effects of study duration on priming and recognition reveal distinct neural substrates.Front Hum Neurosci. 2010 Dec 13;4:227. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2010.00227. eCollection 2010. Front Hum Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21179585 Free PMC article.
-
Conjunction errors and semantic transparency.Mem Cognit. 2010 Jan;38(1):47-56. doi: 10.3758/MC.38.1.47. Mem Cognit. 2010. PMID: 19966238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggleton JP, Brown MW. Episode memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal–anterior thalamic axis. Behavioral Brain Science. 1999;22:425–443. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JR. Language, memory, and thought. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1976.
-
- Anderson JR, Reder LM. An elaborative processing explanation of depth of processing. In: Cermak LS, Craik FIM, editors. Levels of processing in human memory. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1979. pp. 385–403.
-
- Arndt J, Passannante A, Hirshman E. The effect of midazolam on implicit and explicit memory in category exemplar production and cued recall. Memory. 2004;12:158–173. - PubMed
-
- Baars BJ, Gage NM, editors. Cognition, brain, and consciousness: Introduction to cognitive neuroscience. New York: Academic Press; 2007.

