Verbal working memory and language production: Common approaches to the serial ordering of verbal information
- PMID: 19210053
- PMCID: PMC3000524
- DOI: 10.1037/a0014411
Verbal working memory and language production: Common approaches to the serial ordering of verbal information
Erratum in
- Psychol Bull. 2010 May;136(3):350
Abstract
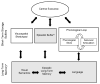
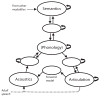
Verbal working memory (WM) tasks typically involve the language production architecture for recall; however, language production processes have had a minimal role in theorizing about WM. A framework for understanding verbal WM results is presented here. In this framework, domain-specific mechanisms for serial ordering in verbal WM are provided by the language production architecture, in which positional, lexical, and phonological similarity constraints are highly similar to those identified in the WM literature. These behavioral similarities are paralleled in computational modeling of serial ordering in both fields. The role of long-term learning in serial ordering performance is emphasized, in contrast to some models of verbal WM. Classic WM findings are discussed in terms of the language production architecture. The integration of principles from both fields illuminates the maintenance and ordering mechanisms for verbal information.
Figures
References
-
- Aldridge JW, Farrell MT. Long-term recency effects in free recall. American Journal of Psychology. 1977;90:475–479.
-
- Allport A. Auditory-verbal short-term memory and conduction aphasia. In: Buoma H, Bouwhuis DG, editors. Attention and Performance X: Control of Language Processes. London: Erlbaum; 1984. pp. 313–326.
-
- Baars BJ, Motley MT, MacKay DG. Output editing lexical status in artificially elicited slips of the tongue. Journal of Verbal Learning & Verbal Behavior. 1975;14:382–391.
-
- Baddeley AD. Immediate memory and the “perception” of letter sequences. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology. 1964;16:364–367.

