Nuclear lamins: key regulators of nuclear structure and activities
- PMID: 19210577
- PMCID: PMC4496104
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00676.x
Nuclear lamins: key regulators of nuclear structure and activities
Abstract
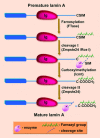
The nuclear lamina is a proteinaceous structure located underneath the inner nuclear membrane (INM), where it associates with the peripheral chromatin. It contains lamins and lamin-associated proteins, including many integral proteins of the INM, chromatin modifying proteins, transcriptional repressors and structural proteins. A fraction of lamins is also present in the nucleoplasm, where it forms stable complexes and is associated with specific nucleoplasmic proteins. The lamins and their associated proteins are required for most nuclear activities, mitosis and for linking the nucleoplasm to all major cytoskeletal networks in the cytoplasm. Mutations in nuclear lamins and their associated proteins cause about 20 different diseases that are collectively called laminopathies'. This review concentrates mainly on lamins, their structure and their roles in DNA replication, chromatin organization, adult stem cell differentiation, aging, tumorogenesis and the lamin mutations leading to laminopathic diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Stuurman N, Heins S, Aebi U. Nuclear lamins: their structure, assembly, and interactions. J Struct Biol. 1998;122:42–66. - PubMed
-
- Herrmann H, Aebi U. Intermediate filaments: molecular structure, assembly mechanism, and integration into functionally distinct intracellular scaffolds. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;74:749–89. - PubMed
-
- Krimm I, Ostlund C, Gilquin B, Couprie J, Hossenlopp P, Mornon JP, Bonne G, Courvalin JC, Worman HJ, Zinn-Justin S. The Ig-like structure of the C-terminal domain of lamin a/c, mutated in muscular dystrophies, cardiomyopathy, and partial lipodystrophy. Structure. 2002;10:811–23. - PubMed
-
- Gerace L, Blobel G. The nuclear envelope lamina is reversibly depolymerized during mitosis. Cell. 1980;19:277–87. - PubMed
-
- Rusiñol AE, Sinensky MS. Farnesylated lamins, progeroid syndromes and farnesyl transferase inhibitors. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:3265–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

