Medial gastrocnemius myoelectric control of a robotic ankle exoskeleton
- PMID: 19211321
- PMCID: PMC2819404
- DOI: 10.1109/TNSRE.2008.2008285
Medial gastrocnemius myoelectric control of a robotic ankle exoskeleton
Abstract
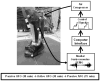
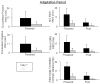
A previous study from our laboratory showed that when soleus electromyography was used to control the amount of plantar flexion assistance from a robotic ankle exoskeleton, subjects significantly reduced their soleus activity to quickly return to normal gait kinematics. We speculated that subjects were primarily responding to the local mechanical assistance of the exoskeleton rather than directly attempting to reduce exoskeleton mechanical power via decreases in soleus activity. To test this observation we studied ten healthy subjects walking on a treadmill at 1.25 m/s while wearing a robotic exoskeleton proportionally controlled by medial gastrocnemius activation. We hypothesized that subjects would primarily decrease soleus activity due to its synergistic mechanics with the exoskeleton. Subjects decreased medial gastrocnemius recruitment by 12% ( p < 0.05 ) but decreased soleus recruitment by 27% ( p < 0.05). In agreement with our hypothesis, the primary reduction in muscle activity was not for the control muscle (medial gastrocnemius) but for the anatomical synergist to the exoskeleton (soleus). These findings indicate that anatomical morphology needs to be considered carefully when designing software and hardware for robotic exoskeletons.
Figures







References
-
- Colombo G, Wirz M, Dietz V. Driven gait orthosis for improvement of locomotor training in paraplegic patients. Spinal Cord. 2001;39:252–255. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal SK, Banala SK, Fattah A, Sangwan V, Krishnamoorthy V, Scholz JP, Hsu WL. Assessment of motion of a swing leg and gait rehabilitation with a gravity balancing exoskeleton. IEEE Transactions of Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering. 2007;15:410–20. - PubMed
-
- Veneman JF, Kruidhof R, Hekman EE, Ekkelenkamp R, Van Asseldonk EH, van der Kooij H. Design and evaluation of the LOPES exoskeleton for interactive gait rehabilitation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering. 2007;15:379–86. - PubMed

