Gender differences in stroke incidence and poststroke disability in the Framingham heart study
- PMID: 19211484
- PMCID: PMC2676725
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.542894
Gender differences in stroke incidence and poststroke disability in the Framingham heart study
Abstract
Background and purpose: Stroke is emerging as a major public health problem for women, as it is for men. Controversy persists regarding gender differences in stroke incidence, severity, and poststroke disability.
Methods: Participants in the Framingham Original (n=5119; 2829 women) and Offspring (n=4957, 2565 women) cohorts who were 45 years and stroke-free were followed to first incident stroke. Gender-specific outcome measures were adjusted for the Framingham Stroke Risk Profile components.
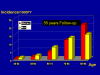
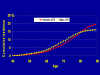
Results: We observed 1136 incident strokes (638 in women) over 56 years of follow-up. Women were significantly (P<0.001) older (75.1 versus 71.1 years for men) at their first-ever stroke, had a higher stroke incidence above 85 years of age, lower at all other ages, and a higher lifetime risk of stroke at all ages. There was no significant difference in stroke subtype, stroke severity, and case fatality rates between genders. Women were significantly (P<0.01) more disabled before stroke and in the acute phase of stroke in dressing (59% versus 37%), grooming (57% versus 34%), and transfer from bed to chair (59% versus 35%). At 3 to 6 months poststroke women were more disabled, more likely to be single, and 3.5 times more likely to be institutionalized (P<0.01).
Conclusions: These results from the Framingham Heart Study (FHS) support the existence of gender-differences in stroke incidence, lifetime risk (LTR) of stroke, age at first stroke, poststroke disability, and institutionalization rates. Prestroke disability and sociodemographic factors may contribute to the high rate of institutionalization and poorer outcome observed in women.
Figures
References
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern SM, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, McDermott M, Meigs J, Moy C, Nichol G, O’Donnell C, Roger V, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wilson M, Hong Y. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2008 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2008;117:e25–146. - PubMed
-
- Bousser MG. Stroke in women: the 1997 Paul Dudley White International Lecture. Circulation. 1999;99:463–467. - PubMed
-
- Seshadri S, Beiser A, Kelly-Hayes M, Kase CS, Au R, Kannel WB, Wolf PA. The lifetime risk of stroke: estimates from the Framingham Study. Stroke. 2006;37:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Kelly-Hayes M, Beiser A, Kase CS, Scaramucci A, D’Agostino RB, Wolf PA. The influence of gender and age on disability following ischemic stroke: the Framingham study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003;12:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Di CA, Lamassa M, Baldereschi M, Pracucci G, Basile AM, Wolfe CD, Giroud M, Rudd A, Ghetti A, Inzitari D. Sex differences in the clinical presentation, resource use, and 3-month outcome of acute stroke in Europe: data from a multicenter multinational hospital-based registry. Stroke. 2003;34:1114–1119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical