Characterization of inhibitory anti-insulin-like growth factor receptor antibodies with different epitope specificity and ligand-blocking properties: implications for mechanism of action in vivo
- PMID: 19211557
- PMCID: PMC2665079
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M809709200
Characterization of inhibitory anti-insulin-like growth factor receptor antibodies with different epitope specificity and ligand-blocking properties: implications for mechanism of action in vivo
Abstract
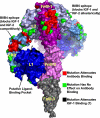
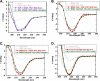
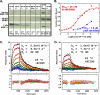
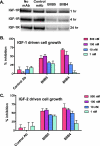
Therapeutic antibodies directed against the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) have recently gained significant momentum in the clinic because of preliminary data generated in human patients with cancer. These antibodies inhibit ligand-mediated activation of IGF-1R and the resulting down-stream signaling cascade. Here we generated a panel of antibodies against IGF-1R and screened them for their ability to block the binding of both IGF-1 and IGF-2 at escalating ligand concentrations (>1 microm) to investigate allosteric versus competitive blocking mechanisms. Four distinct inhibitory classes were found as follows: 1) allosteric IGF-1 blockers, 2) allosteric IGF-2 blockers, 3) allosteric IGF-1 and IGF-2 blockers, and 4) competitive IGF-1 and IGF-2 blockers. The epitopes of representative antibodies from each of these classes were mapped using a purified IGF-1R library containing 64 mutations. Most of these antibodies bound overlapping surfaces on the cysteine-rich repeat and L2 domains. One class of allosteric IGF-1 and IGF-2 blocker was identified that bound a separate epitope on the outer surface of the FnIII-1 domain. Using various biophysical techniques, we show that the dual IGF blockers inhibit ligand binding using a spectrum of mechanisms ranging from highly allosteric to purely competitive. Binding of IGF-1 or the inhibitory antibodies was associated with conformational changes in IGF-1R, linked to the ordering of dynamic or unstructured regions of the receptor. These results suggest IGF-1R uses disorder/order within its polypeptide sequence to regulate its activity. Interestingly, the activity of representative allosteric and competitive inhibitors on H322M tumor cell growth in vitro was reflective of their individual ligand-blocking properties. Many of the antibodies in the clinic likely adopt one of the inhibitory mechanisms described here, and the outcome of future clinical studies may reveal whether a particular inhibitory mechanism leads to optimal clinical efficacy.
Figures





References
-
- Chitnis, M. M., Yuen, J. S. P., Protheroe, A. S., Pollak, M., and Macaulay, V. M. (2008) Clin. Cancer Res. 14 6364-6370 - PubMed
-
- Pollak, M. N., Schernhammer, E. S., and Hankinson, S. E. (2004) Nat. Rev. Cancer 4 505-518 - PubMed
-
- Adams, T. E., McKern, N. M., and Ward, C. W. (2004) Growth Factors 22 89-95 - PubMed
-
- Lawrence, M. C., McKern, N. M., and Ward, C. W. (2007) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 17 699-705 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

