Depletion of the poly(C)-binding proteins alphaCP1 and alphaCP2 from K562 cells leads to p53-independent induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CDKN1A) and G1 arrest
- PMID: 19211566
- PMCID: PMC2666552
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806986200
Depletion of the poly(C)-binding proteins alphaCP1 and alphaCP2 from K562 cells leads to p53-independent induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CDKN1A) and G1 arrest
Abstract
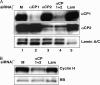
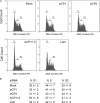
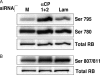
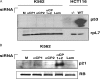
The alpha-globin poly(C)-binding proteins (alphaCPs) comprise an abundant and widely expressed set of K-homolog domain RNA-binding proteins. alphaCPs regulate the expression of a number of cellular and viral mRNAs at the levels of splicing, stability, and translation. Previous surveys have identified 160 mRNAs that are bound by alphaCP in the human hematopoietic cell line, K562. To explore the functions of these alphaCP/mRNA interactions, we identified mRNAs whose levels are altered in K562 cells acutely depleted of the two major alphaCP proteins, alphaCP1 and alphaCP2. Microarray analysis identified 27 mRNAs that are down-regulated and 14 mRNAs that are up-regulated in the alphaCP1/2-co-depleted cells. This alphaCP1/2 co-depletion was also noted to inhibit cell proliferation and trigger a G(1) cell cycle arrest. Targeted analysis of genes involved in cell cycle control revealed a marked increase in p21(WAF) mRNA and protein. Analysis of mRNP complexes in K562 cells demonstrates in vivo association of p21(WAF) mRNA with alphaCP1 and alphaCP2. In vitro binding assays indicate that a 127-nucleotide region of the 3'-untranslated region of p21(WAF) interacts with both alphaCP1 and alphaCP2, and co-depletion of alphaCP1/2 results in a marked increase in p21(WAF) mRNA half-life. p21(WAF) induction and G(1) arrest in the alphaCP1/2-co-depleted cells occur in the absence of p53 and are not observed in cells depleted of the individual alphaCP isoforms. The apparent redundancy in the actions of alphaCP1 and alphaCP2 upon p21(WAF) expression correlates with a parallel redundancy in their effects on cell cycle control. These data reveal a pivotal role for alphaCP1 and alphaCP2 in a p53-independent pathway of p21(WAF) control and cell cycle progression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel set of nuclear localization signals determine distributions of the alphaCP RNA-binding proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Dec;23(23):8405-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.23.8405-8415.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14612387 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of mRNAs associated with alphaCP2-containing RNP complexes.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Oct;23(19):7055-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.19.7055-7067.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12972621 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and RNA binding properties of the polycytidylate-binding proteins alphaCP1 and alphaCP2.Methods. 1999 Jan;17(1):84-91. doi: 10.1006/meth.1998.0710. Methods. 1999. PMID: 10075886
-
Posttranscriptional regulation of p53 and its targets by RNA-binding proteins.Curr Mol Med. 2008 Dec;8(8):845-9. doi: 10.2174/156652408786733748. Curr Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 19075680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intricacies of p21 phosphorylation: protein/protein interactions, subcellular localization and stability.Cell Cycle. 2006 Jun;5(12):1313-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.12.2863. Epub 2006 Jun 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16775416 Review.
Cited by
-
Specific enrichment of the RNA-binding proteins PCBP1 and PCBP2 in chief cells of the murine gastric mucosa.Gene Expr Patterns. 2014 Mar;14(2):78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Gene Expr Patterns. 2014. PMID: 24480778 Free PMC article.
-
RNA binding proteins PCBP1 and PCBP2 regulate pancreatic β cell translation.Mol Metab. 2025 Aug;98:102175. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.102175. Epub 2025 May 30. Mol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40451383 Free PMC article.
-
The 3' untranslated region of the rabies virus glycoprotein mRNA specifically interacts with cellular PCBP2 protein and promotes transcript stability.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033561. Epub 2012 Mar 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22438951 Free PMC article.
-
PCBP1 depletion promotes tumorigenesis through attenuation of p27Kip1 mRNA stability and translation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 7;37(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0840-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30086790 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding Protein PCBP2 Regulates p73 Expression and p73-dependent Antioxidant Defense.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 29;291(18):9629-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.712125. Epub 2016 Feb 23. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26907686 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

