A mouse model for Meckel syndrome type 3
- PMID: 19211713
- PMCID: PMC2663826
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008040412
A mouse model for Meckel syndrome type 3
Abstract
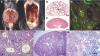
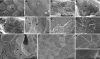
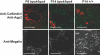
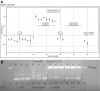
Meckel-Gruber syndrome type 3 (MKS3; OMIM 607361) is a severe autosomal recessive disorder characterized by bilateral polycystic kidney disease. Other malformations associated with MKS3 include cystic changes in the liver, polydactyly, and brain abnormalities (occipital encephalocele, hydrocephalus, and Dandy Walker-type cerebellar anomalies). The disorder is hypothesized to be caused by defects in primary cilia. In humans, the underlying mutated gene, TMEM67, encodes transmembrane protein 67, also called meckelin (OMIM 609884), which is an integral protein of the renal epithelial cell and membrane of the primary cilium. Here, we describe a spontaneous deletion of the mouse ortholog, Tmem67, which results in polycystic kidney disease and death by 3 wk after birth. Hydrocephalus also occurs in some mutants. We verified the mutated gene by transgenic rescue and characterized the phenotype with microcomputed tomography, histology, scanning electron microscopy, and immunohistochemistry. This mutant provides a mouse model for MKS3 and adds to the growing set of mammalian models essential for studying the role of the primary cilium in kidney function.
Figures




References
-
- Grantham JJ, Nair V, Winklhofer F: Cystic disease of the kidney. In: Brenner & Rector's The Kidney, Vol. 2, 6th Ed., edited by Brenner BM, Philadelphia, WB Saunders Co., 2000, pp 1699–1730
-
- Wilson PD: Polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 350: 151–164, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Guay-Woodford LM, Desmond RA: Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: The clinical experience in North America. Pediatrics 111: 1072–1080, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Torres VE, Harris PC: Mechanisms of disease: Autosomal dominant and recessive polycystic kidney disease. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2: 40–55, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Esteban MA, Harten SK, Tran MG, Maxwell PH: Formation of primary cilia in the renal epithelium is regulated by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 1801–1806, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

