Neural activity associated with the passive prediction of ambiguity and risk for aversive events
- PMID: 19211872
- PMCID: PMC2688025
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4578-08.2009
Neural activity associated with the passive prediction of ambiguity and risk for aversive events
Abstract
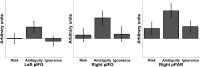
In economic decision making, outcomes are described in terms of risk (uncertain outcomes with certain probabilities) and ambiguity (uncertain outcomes with uncertain probabilities). Humans are more averse to ambiguity than to risk, with a distinct neural system suggested as mediating this effect. However, there has been no clear disambiguation of activity related to decisions themselves from perceptual processing of ambiguity. In a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) experiment, we contrasted ambiguity, defined as a lack of information about outcome probabilities, to risk, where outcome probabilities are known, or ignorance, where outcomes are completely unknown and unknowable. We modified previously learned pavlovian CS+ stimuli such that they became an ambiguous cue and contrasted evoked brain activity both with an unmodified predictive CS+ (risky cue), and a cue that conveyed no information about outcome probabilities (ignorance cue). Compared with risk, ambiguous cues elicited activity in posterior inferior frontal gyrus and posterior parietal cortex during outcome anticipation. Furthermore, a similar set of regions was activated when ambiguous cues were compared with ignorance cues. Thus, regions previously shown to be engaged by decisions about ambiguous rewarding outcomes are also engaged by ambiguous outcome prediction in the context of aversive outcomes. Moreover, activation in these regions was seen even when no actual decision is made. Our findings suggest that these regions subserve a general function of contextual analysis when search for hidden information during outcome anticipation is both necessary and meaningful.
Figures
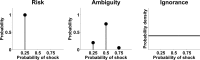



References
-
- Andersson JL, Hutton C, Ashburner J, Turner R, Friston K. Modeling geometric deformations in EPI time series. Neuroimage. 2001;13:903–919. - PubMed
-
- Becker SW, Brownson FO. What price ambiguity? Or the role of ambiguity in decision making. J Polit Econ. 1964;72:62–73.
-
- Bernoulli D. Specimen theoriae novae de mensura sortis. Commentarii Academiae Scientiarum Imperialis Petropolitanae. 1738;5:175–192.
-
- Büchel C, Morris J, Dolan RJ, Friston KJ. Brain systems mediating aversive conditioning: an event-related fMRI study. Neuron. 1998;20:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Camerer C. Individual decision making. In: Kagel JH, Roth AE, editors. Handbook of experimental economics. Princeton: Princeton UP; 1995. pp. 587–704.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
