Involvement of SRC family kinases in substance P-induced chemokine production in mouse pancreatic acinar cells and its significance in acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 19211920
- PMCID: PMC2672875
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.108.148684
Involvement of SRC family kinases in substance P-induced chemokine production in mouse pancreatic acinar cells and its significance in acute pancreatitis
Abstract
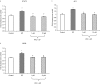
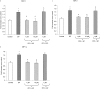
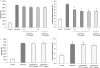
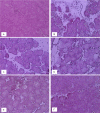
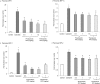
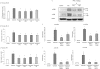
Substance P is known to play a key role in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Src family kinases (SFKs) are known to be involved in cytokine signaling. However, the involvement of SFKs in substance P-induced chemokine production and its role in acute pancreatitis have not been investigated yet. To that end, we have used primary preparations of mouse pancreatic acinar cells as our model to show that substance P/neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) induced activation of SFKs. SFKs mediated the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases [extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK)], transcription factors [signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3, nuclear factor (NF) kappaB, activator protein-1 (AP-1)], and production of chemokines in pancreatic acinar cells. We further tested the significance of the SFK signaling pathway in acute pancreatitis. Our results show, for the first time, that treatment of mice with the potent and selective SFK inhibitor PP2 [4-amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-(t-butyl) pyrazolo [3,4-D] pyrimidine], but not its negative inhibitor PP3 (4-amino-7-phenylpyrazol [3,4-D] pyrimidine), reduced the severity of pancreatitis. This was proven by significant attenuation of hyperamylasemia, pancreatic myeloperoxidase activity, chemokines, and water content. Histological evidence of diminished pancreatic injury also confirmed the protective effect of the inhibition of SFKs. Moreover, treatment with the substance P receptor antagonist CP96345 [(2S,3S)-cis-2-(diphenylmethyl)-N-((2-methoxyphenyl)-methyl)-1-azabicyclo(2.2.2.)-octan-3-amine] attenuated acute pancreatitis-induced activation of SFKs, ERK, JNK, STAT3, NFkappaB, and AP-1. The proposed signaling pathway through which substance P mediates acute pancreatitis is through substance P/NK1R-SFKs-(ERK, JNK)-(STAT3, NFkappaB, AP-1) chemokines. In light of our study, we propose that drugs targeting the substance P-mediated signaling pathways could prove beneficial in improving treatment efficacy in acute pancreatitis.
Figures
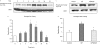
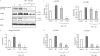
References
-
- Akira S (2000) Roles of STAT3 defined by tissue-specific gene targeting. Oncogene 19 2607-2611. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama C, Yuguchi T, Nishio M, Tomishima T, Fujinaka T, Taniguchi M, Nakajima Y, Kohmura E, and Yoshimine T (2004) Src family kinase inhibitor PP1 reduces secondary damage after spinal cord compression in rats. J Neurotrauma 21 923-931. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong SC (2004) Protein kinase activation and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res 61 427-436. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia M (2002) Novel therapeutic targets for acute pancreatitis and associated multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 1 343-351. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia M, Brady M, Kang YK, Costello E, Newton DJ, Christmas SE, Neoptolemos JP, and Slavin J (2002) MCP-1 but not CINC synthesis is increased in rat pancreatic acini in response to cerulein hyperstimulation. Am J Physiol Gastro-intest Liver Physiol 282 G77-G85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

