Urinary biomarkers for sensitive and specific detection of acute kidney injury in humans
- PMID: 19212447
- PMCID: PMC2638059
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2008.00053.x
Urinary biomarkers for sensitive and specific detection of acute kidney injury in humans
Abstract
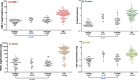
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with high morbidity and mortality. The lack of sensitive and specific injury biomarkers has greatly impeded the development of therapeutic strategies to improve outcomes of AKI.The unique objective of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of nine urinary biomarkers of AKI-kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL), interleukin-18 (IL-18), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), cystatin C (Cys), N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), chemokine interferon-inducible protein 10 (IP-10; CXCL10), and total protein-in a cross-sectional comparison of 204 patients with or without AKI.Median urinary concentrations of each biomarker were significantly higher in patients with AKI than in those without AKI (p < 0.001). The area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC-ROC) for the combination of biomarkers using a logic regression model [risk score of 2.93*(NGAL > 5.72 and HGF > 0.17) + 2.93*(PROTEIN > 0.22) -2*(KIM < 0.58)] was greater (0.94) than individual biomarker AUC-ROCs. Age-adjusted levels of urinary KIM-1, NAG, HGF, VEGF, and total protein were significantly higher in patients who died or required renal replacement therapy (RRT) when compared to those who survived and did not require RRT.Our results demonstrate the comparative value of multiple biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of AKI.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; biomarkers; hepatocyte growth factor; kidney injury molecule-1; neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin.
Figures


References
-
- Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005; 16: 3365–3370. - PubMed
-
- Star RA. Treatment of acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1998; 54: 1817–1831. - PubMed
-
- Woosley RL, Cossman J. Drug development and the FDAs Critical Path Initiative. Gin Pharmacol Ther. 2007; 81: 129–133. - PubMed
-
- Hewitt SM, Dear J, Star RA. Discovery of protein biomarkers for renal diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15: 1677–1689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 DK075941/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 ES016723/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039773/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK72831/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R33 DK074099/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK074099/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK74099/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 ES016723/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK039773/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK39773/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99/R00 ES16723/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

