Evaluation of Treatments in Patients with Nocturnal Bruxism on Bite Force and Occlusal Contact Area: A preliminary report
- PMID: 19212534
- PMCID: PMC2634782
Evaluation of Treatments in Patients with Nocturnal Bruxism on Bite Force and Occlusal Contact Area: A preliminary report
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to investigate the short-term effects of occlusal splint therapy and tricyclic antidepressants on the bite force and occlusal contact area of patients presenting with nocturnal bruxism.
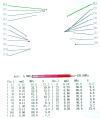
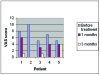
Methods: A maxillary full-coverage hard acrylic splint was applied to the five patients (Group S). Five patients took a tricyclic antidepressant (Amitriptiline HCl, 10 mg/day) for 3 months (Group A) and a control group (Group C) comprising of 10 dental school students with normal occlusion was also formed. Using a Dental Prescale (Fuji Photo Film Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) and an Occluzer computer (FPD703, Fuji Photo Film Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) the bite force and occlusal contact area were measured. The evaluations were made just before the treatment and at 1 month and 3 months of treatment.
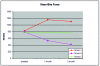
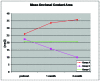
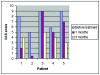
Results: The bite force and occlusal contact area before treatment in study Groups A and S were found to be higher than those in the Group C. Furthermore, the bite force and occlusal contact area increased during treatment in Group A whilst they decreased in Group S. Bite force and occlusal contact area in Group S were lower at both 1 month and 3 months of treatment than in Group C.
Conclusions: It could be tentatively suggested that occlusal splint therapy may be more effective than tricyclic antidepressant in the treatment of bruxism. Further investigations of this measurement method involving larger study populations and a longer follow-up period are needed.
Keywords: Antidepressant; Bite force; Bruxism; Occlusal contact area; Splint.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Clinical evaluation of measuring system of occlusal force].Kokubyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1994 Sep;61(3):437-45. doi: 10.5357/koubyou.61.437. Kokubyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1994. PMID: 7806939 Japanese.
-
The amount of mandibular setback influence on occlusal force following sagittal split ramus osteotomy.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015 Nov;43(9):1743-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2015.08.015. Epub 2015 Sep 5. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 26431610
-
Bite force and occlusal contact area changes following mandibular widening using distraction osteogenesis.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006 Apr;101(4):432-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.017. Epub 2006 Jan 19. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006. PMID: 16545704 Clinical Trial.
-
Occlusal Splints and Periodontal/Implant Therapy.J Int Acad Periodontol. 2019 Jan 31;21(1):45-50. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2019. PMID: 31522162 Review.
-
The Effect of Patient Specific Factors on Occlusal Forces Generated: Best Evidence Consensus Statement.J Prosthodont. 2021 Apr;30(S1):52-60. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13334. J Prosthodont. 2021. PMID: 33474770 Review.
Cited by
-
Short-term effect of material type and thickness of occlusal splints on maximum bite force and sleep quality in patients with sleep bruxism: a randomized controlled clinical trial.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Aug;27(8):4313-4322. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05049-4. Epub 2023 May 2. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 37127807 Clinical Trial.
-
Occlusal overload with dental implants: a review.Int J Implant Dent. 2019 Jul 23;5(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s40729-019-0180-8. Int J Implant Dent. 2019. PMID: 31332553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Occlusion and Biomechanical Risk Factors in Implant-Supported Full-Arch Fixed Dental Prostheses-Narrative Review.J Pers Med. 2025 Feb 7;15(2):65. doi: 10.3390/jpm15020065. J Pers Med. 2025. PMID: 39997342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3Shape Digital Design Software in Splints Creation-A Pilot Study.Eur J Dent. 2022 Oct;16(4):815-819. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1739546. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Eur J Dent. 2022. PMID: 34952555 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) for the Recovery of Oral Function after Orthognathic Surgery.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 7;11(12):3268. doi: 10.3390/jcm11123268. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35743339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruxism, in: The Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms(ed7) J Prosthet Dent. 1999;81:5. - PubMed
-
- Israel HA, Diamond B, Saed- Nejad F, Raatcliffe A. The relationship between parafunctional masticatory activity and arthroscopically diagnosed temporomandibular joint pathology. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999;57:1034–1039. - PubMed
-
- Silverman S, Eversole LR, Trulove EL. Essentials of Oral Medicine. Hamilton-London: BC Decker Inc; 2001.
-
- Bowley JF, Marx DB. Masticatory muscle activity assessment and reliability of a portable electromyographic instrument. J Prosthet Dent. 2001;85:252–260. - PubMed
-
- Janal MN, Raphael KG, Klausner J, Teaford M. The role of tooth-grinding in the maintenance of myofascial face pain: A test of alternate models. Pain Medicine. 2007;8:486–496. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
