Retinoids induce differentiation and downregulate telomerase activity and N-Myc to increase sensitivity to flavonoids for apoptosis in human malignant neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells
- PMID: 19212680
- PMCID: PMC2643361
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo_00000201
Retinoids induce differentiation and downregulate telomerase activity and N-Myc to increase sensitivity to flavonoids for apoptosis in human malignant neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells
Abstract
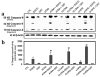
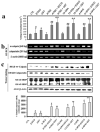
Human malignant neuroblastoma is characterized by poor differentiation and uncontrolled proliferation of immature neuroblasts. Retinoids such as all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA), 13-cis-retinoic acid (13-CRA), and N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide (4-HPR) at low doses are capable of inducing differentiation, while flavonoids such as (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and genistein (GST) at relatively high dose can induce apoptosis. We used combination of retinoid and flavonoid for controlling growth of malignant neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Cells were treated with a retinoid (1 microM ATRA, 1 microM 13-CRA, or 0.5 microM 4-HPR) for 7 days and then with a flavonoid (25 microM EGCG or 25 microM GST) for 24 h. Treatment of cells with a low dose of a retinoid for 7 days induced neuronal differentiation with downregulation of telomerase activity and N-Myc but overexpression of neurofilament protein (NFP) and subsequent treatment with a relatively high dose of a flavonoid for 24 h increased apoptosis in the differentiated cells. Besides, retinoids reduced the levels of inflammatory and angiogenic factors. Apoptosis was associated with increases in intracellular free [Ca2+], Bax expression, cytochrome c release from mitochondria and activities of calpain and caspases. Decreases in expression of calpastatin (endogenous calpain inhibitor) and baculovirus inhibitor-of-apoptosis repeat containing (BIRC) proteins (endogenous caspase inhibitors) favored apoptosis. Treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with EGCG activated caspase-8, indicating induction of the receptor-mediated pathway of apoptosis. Based on our observation, we conclude that combination of a retinoid and a flavonoid worked synergistically for controlling the malignant growth of human neuroblastoma cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mechanism of apoptosis with the involvement of calpain and caspase cascades in human malignant neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells exposed to flavonoids.Int J Cancer. 2006 Dec 1;119(11):2575-85. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22228. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16988947
-
Synergistic efficacy of sorafenib and genistein in growth inhibition by down regulating angiogenic and survival factors and increasing apoptosis through upregulation of p53 and p21 in malignant neuroblastoma cells having N-Myc amplification or non-amplification.Invest New Drugs. 2010 Dec;28(6):812-24. doi: 10.1007/s10637-009-9324-7. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Invest New Drugs. 2010. PMID: 19777160 Free PMC article.
-
N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl) retinamide induced both differentiation and apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G and U87MG cells.Brain Res. 2008 Aug 28;1227:207-15. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.045. Epub 2008 Jun 21. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18602901 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoids induced astrocytic differentiation with down regulation of telomerase activity and enhanced sensitivity to taxol for apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G and U87MG cells.J Neurooncol. 2008 Mar;87(1):9-22. doi: 10.1007/s11060-007-9485-1. Epub 2007 Nov 7. J Neurooncol. 2008. PMID: 17987264
-
Molecular mechanisms of the combination of retinoid and interferon-gamma for inducing differentiation and increasing apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G and U87MG cells.Neurochem Res. 2009 Jan;34(1):87-101. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9669-x. Epub 2008 Mar 27. Neurochem Res. 2009. PMID: 18368485 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Transcriptional Complex Sp1/KMT2A by Up-Regulating Restrictive Element 1 Silencing Transcription Factor Accelerates Methylmercury-Induced Cell Death in Motor Neuron-Like NSC34 Cells Overexpressing SOD1-G93A.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 26;15:771580. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.771580. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34899171 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR ATP-competitive inhibitor INK128 inhibits neuroblastoma growth via blocking mTORC signaling.Apoptosis. 2015 Jan;20(1):50-62. doi: 10.1007/s10495-014-1066-0. Apoptosis. 2015. PMID: 25425103 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid and cAMP inhibit rat hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and enhance cell differentiation.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012 Aug;45(8):721-9. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2012007500087. Epub 2012 May 24. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012. PMID: 22618858 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl-2 inhibitor and apigenin worked synergistically in human malignant neuroblastoma cell lines and increased apoptosis with activation of extrinsic and intrinsic pathways.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Oct 30;388(4):705-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.071. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19695221 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic enhancement of anticancer effects on numerous human cancer cell lines treated with the combination of EGCG, other green tea catechins, and anticancer compounds.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Sep;141(9):1511-22. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1899-5. Epub 2014 Dec 28. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25544670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brodeur GM. Meeting summary for advances in neuroblastoma research-2000. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2000;35:727–728. - PubMed
-
- Guzhova I, Hultquist A, Cetinkaya C, Nilsson K, Påhlman S, Larsson LG. Interferon-gamma cooperates with retinoic acid and phorbol ester to induce differentiation and growth inhibition of human neuroblastoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds CP, Kane DJ, Einhorn PA, Matthay KK, Crouse VL, Wilbur JR, Shurin SB, Seeger RC. Response of neuroblastoma to retinoic acid in vitro and in vivo. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;366:203–211. - PubMed
-
- Veal GJ, Errington J, Redfern CP, Pearson AD, Boddy AV. Influence of isomerisation on the growth inhibitory effects and cellular activity of 13-cis and all-trans retinoic acid in neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002;63:207–215. - PubMed
-
- Lovat PE, Corazzari M, Goranov B, Piacentini M, Redfern CP. Molecular mechanisms of fenretinide-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2004;28:81–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

